111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Ezrin 通过激活 Akt/mTOR 通路并诱导 YAP 易位促进胰腺癌细胞增殖和侵袭
Authors Quan C, Sun J, Lin Z, Jin T, Dong B, Meng Z, Piao J
Received 21 January 2019
Accepted for publication 29 May 2019
Published 12 July 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 6553—6566
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S202342
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Rituraj Purohit
Background: Ezrin and YAP are abnormally expressed in various cancers, and play pivotal roles in cancer initiation and development. However, the mechanisms of Ezrin in pancreatic cancer have not been fully elucidated. In this study, we aimed to elucidate the functions and mechanisms of Ezrin in the pathogenesis of pancreatic cancer.
Methods: Effects of Ezrin deregulation on pancreatic cancer phenotype were determined in Capan-1 and BxPC-3 cells using MTT, colony formation, transwell, wound-healing, and chick chorioallantoic membrane assays. To find out the underlying mechanism of Ezrin, multiple assays were performed to detect the effect of Ezrin on Akt pathway activation and YAP expression. Then, Ezrin and YAP expression was analyzed in pancreatic cancer and normal pancreas samples. Finally, the prognostic value of Ezrin and YAP was evaluated in pancreatic cancer patients.
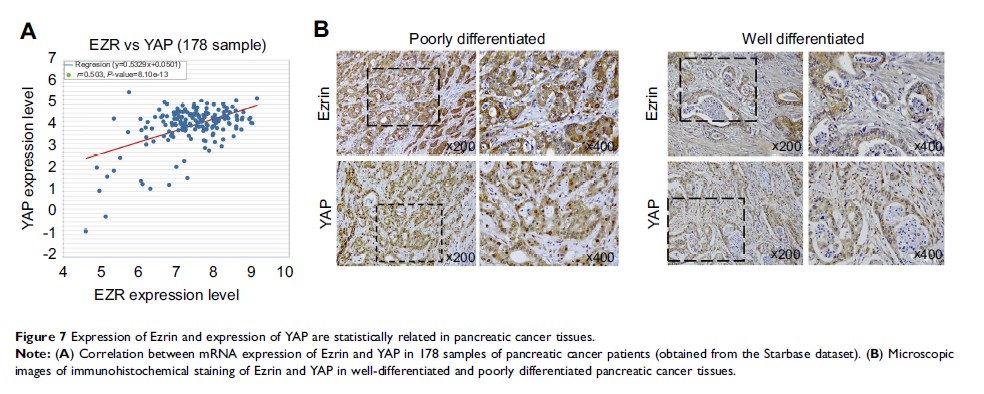
Results: Ezrin promoted proliferation, invasion, epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) progression, and angiogenesis of pancreatic cancers. Mechanistically, Ezrin activated Akt/mTOR pathways and induced YAP phosphorylation and nucleus translocation. The PI3K/Akt pathway inhibitor, rapamycin, and LY294002 could partially attenuate the effect of Ezrin on cell proliferation, invasion, EMT progression, and YAP phosphorylation and translocation. Moreover, both Ezrin and YAP were significantly overexpressed in pancreatic cancer tissues compared with adjacent normal pancreas, and correlated with poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer patients. Multivariate survival analysis showed that Ezrin was an independent prognostic marker for pancreatic cancer. Furthermore, the expression status of Ezrin and YAP had positive correlations in pancreatic cancer tissues.
Conclusion: Ezrin promoted pancreatic cancer proliferation, invasion, migration, and EMT progression, partially through activating the PI3K/Akt pathway, and also regulated YAP phosphorylation and translocation, partially through the PI3K/Akt pathway. Ezrin and YAP were significantly overexpressed in pancreatic cancers, and correlated with poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer patients.
Keywords: Ezrin, YAP, PI3K/Akt pathway, pancreatic cancer, survival