111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

IKBKE 和 TBK1 在 I 期非小细胞肺癌中的表达和预后作用
Authors Wang X, Teng F, Lu J, Mu D, Zhang J, Yu J
Received 11 February 2019
Accepted for publication 27 May 2019
Published 15 July 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 6593—6602
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S204924
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Lu-Zhe Sun
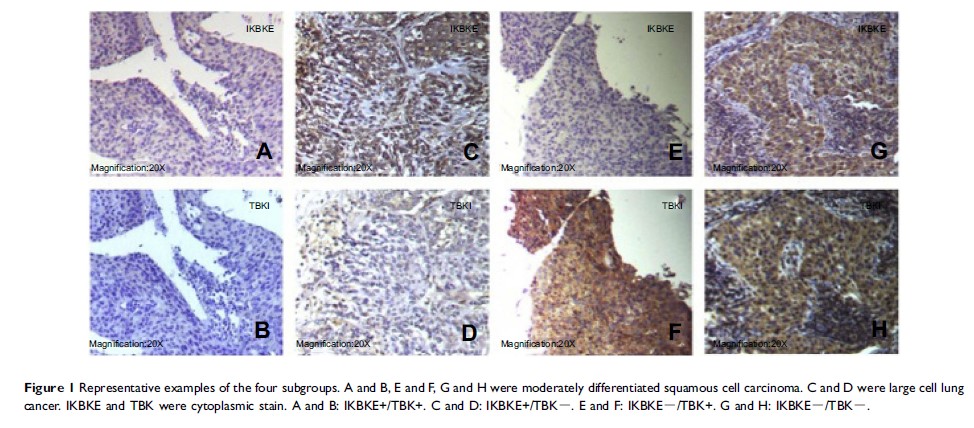
Background: The inhibitors of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit epsilon (IKBKE ) and TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1 ) are important members of the nonclassical IKK family that share the kinase domain. They are important oncogenes for activation of several signaling pathways in several tumors. This study aims to explore the expression of IKBKE and TBK1 and their prognostic role in stage I non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Patients and methods: A total of 142 surgically resected stage I NSCLC patients were enrolled and immunohistochemistry of IKBKE and TBK1 was performed.
Results: IKBKE and TBK1 were expressed in 121 (85.2%) and 114 (80.3%) of stage I NSCLC patients respectively. IKBKE expression was significantly associated with TBK1 expression (P =0.004). Furthermore, multivariate regression analyses showed there was a significant relationship between patients with risk factors, the recurrence pattern of metastasis and IKBKE+/TBK1+ co-expression (P =0.032 and P =0.022, respectively). In Kaplan–Meier survival curve analyses, the IKBKE+/TBK1+ co-expression subgroup was significantly associated with poor overall survival (P =0.014).
Conclusions: This is the first study to investigate the relationship between IKBKE and TBK1 expression and clinicopathologic characteristics in stage I NSCLC patients. IKBKE+/TBK1+ co-expression was significantly obvious in patients with risk factors and with recurrence pattern of distant metastasis. Furthermore, IKBKE+/TBK1+ is also an effective prognostic predictor for poor overall survival.
Keywords: IKBKE, TBK1, NSCLC, prognosis, cancer