111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Hippo YAP 信号在辐射诱导的胶质瘤细胞凋亡中的作用
Authors Xu X, Chen Y, Wang X, Mu X
Received 1 April 2019
Accepted for publication 6 July 2019
Published 9 August 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 7577—7585
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S210825
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Lu-Zhe Sun
Background: Although Hippo/Yes-associated protein (YAP) signaling plays crucial roles in radiation sensitivity and resistance of multiple kinds of cancers, its role in the radiation sensitivity of glioma cells remains unclear. The present study aimed to reveal Hippo/YAP role in the radiation sensitivity of glioma cells.
Methods: Glioma U251 cells were administrated with different doses of irradiation. Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) and flow cytometry assays were used to assess cell viability and apoptosis. Co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) assay was used to assess the interactions between proteins.
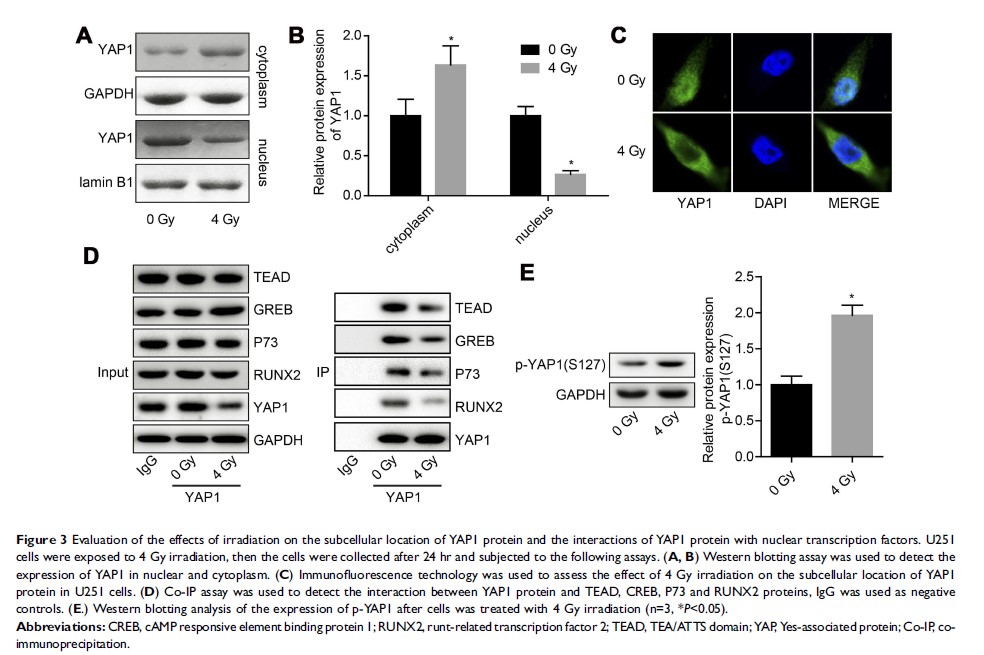
Results: The results showed that irradiation exposure significantly inhibited cell viability and induced cell apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner, as well as decreased YAP1 expression via enhancing RCHY1-mediated YAP1 protein degradation. In addition, we observed that downregulation of YAP1 or RCHY1 weakened the role of irradiation exposure in cell viability inhibition and apoptosis promotion.
Conclusion: Collectively, this study emphasizes the vital role of Hippo/YAP signaling in radiation sensitivity of glioma, that RCHY1-mediated YAP1 protein downregulation is a main mechanism accounting for radiation-induced glioma cell apoptosis. Our study may enrich the theoretical basis of Hippo/YAP signaling as a new target for improving radiation sensitivity in glioma.
Keywords: radiation, Hippo/YAP signaling, ubiquitination, RCHY1, glioma