110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

IL-12 基因疗法可抑制 HCC-Hu-PBL-NOD/SCID 小鼠模型中的肿瘤生长
Authors Zhou ZF, Peng F, Li JY, Ye YB
Received 5 July 2019
Accepted for publication 11 September 2019
Published 20 September 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 7773—7784
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S222097
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Aruna Narula
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of intratumoral IL-12 gene therapy in an HCC-hu-PBL-NOD/SCID mouse model.
Materials and methods: The HCC murine model was generated in NOD/SCID mice, and mice with grafted tumors were injected intraperitoneally with 2 × 107 human peripheral blood lymphocytes 14 days after modeling. After 4 days, mice were randomly divided into the 9597/IL-12 group, the 9597/plasmid group and the PBS group. The changes of tumor volume were measured and mouse peripheral blood was sampled post-treatment for ELISA and CBA analyses, and the grafted tumors were collected 28 days post-treatment for immunohistochemistry, ELISA, CBA and detection of cell cycle and apoptosis.
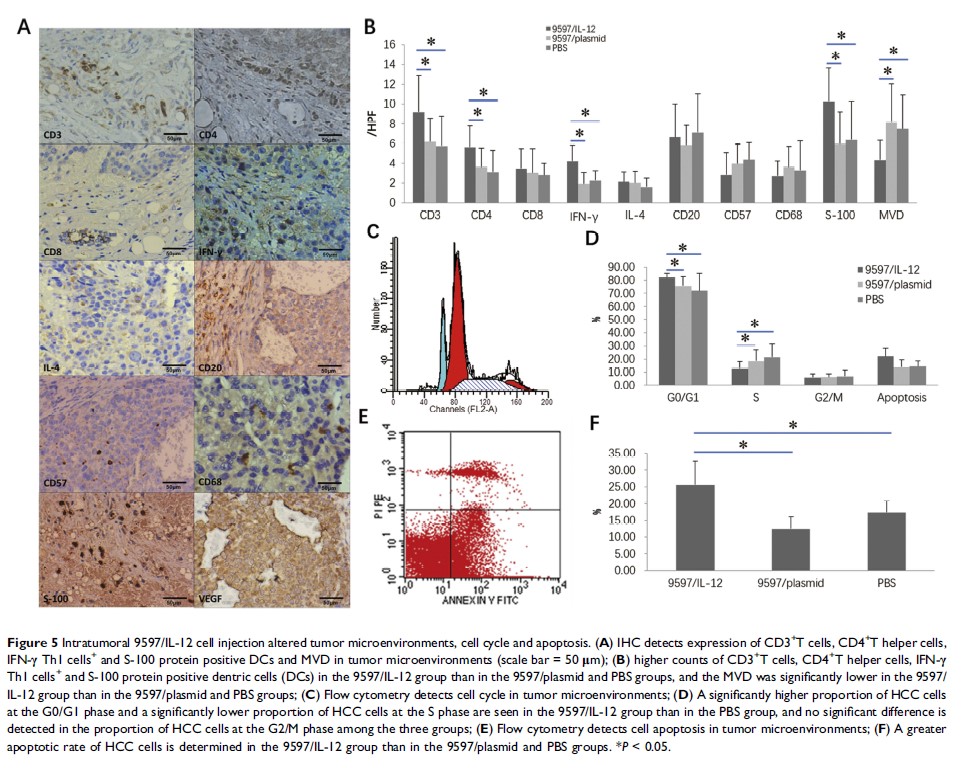
Results: The tumor volume was smaller in the 9597/IL-12 group than in the 9597/plasmid and PBS groups on days 7, 14, 21, and 28 post-treatment (P < 0.05). Higher IL-12 levels were detected in the peripheral blood and the supernatants of grafted tumor homogenates in the 9597/IL-12 group than in the 9597/plasmid and PBS groups 7, 14, 21 and 28 days post-treatment (P < 0.05). IHC revealed higher counts of CD3+T cells, CD4+T helper cells, IFN-γ Th1 cells+ and S-100 protein positive dentric cells and lower MVD in the 9597/IL-12 group than in the 9597/plasmid and PBS groups (P < 0.05). Flow cytometry showed a significantly higher proportion of HCC cells at the G0/G1 phase and a significantly lower proportion of HCC cells at the S phase in the 9597/IL-12 group than in the PBS group (P < 0.05) and a greater apoptotic rate of HCC cells in the 9597/IL-12 group than in the 9597/plasmid and PBS groups (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Intratumoral IL-12 gene therapy may inhibit tumorigenesis with mild adverse effects in a HCC-hu-PBL-NOD/SCID murine model through inhibiting angiogenesis, arresting cells in G0/G1 phase and inducing apoptosis.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, IL-12, gene therapy, efficacy, toxicity