110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-139-5p 通过靶向 TCF4 并抑制 Wnt/β-catenin 信号传导在宫颈癌中发挥肿瘤抑制作用
Authors Ji X, Guo H, Yin S, Du H
Received 15 May 2019
Accepted for publication 30 August 2019
Published 20 September 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 7739—7748
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S215796
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Aruna Narula
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
Objectives: Dysregulation of microRNAs (miRNAs) has been recognized as a crucial biological event in the development of cervical cancer (CC). miR-139-5p was identified as a significant tumor suppressor in multiple human cancers, leaving its roles and mechanisms in CC absolutely unclear. We aimed to investigate the implication of miR-139-5p in CC progression.
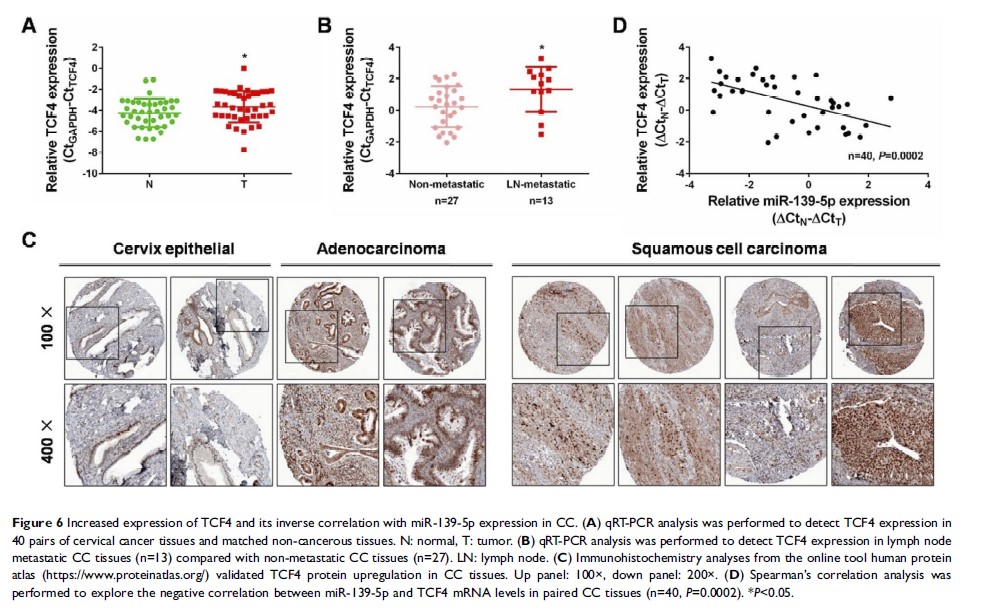
Methods: miR-139-5p expression in 40 paired CC tissues and several cell lines was determined by qRT-PCR firstly. The implications of miR-139-5p in CC cell proliferation and migration were revealed by CCK-8, EdU and transwell assays, respectively. The mechanism underlying the tumor-suppressing roles of miR-139-5p in CC was investigated sequentially by dual luciferase, qRT-PCR, and Western blot analysis. The expression of transcription factor 4 (TCF4), the validated target of miR-139-5p from our experiments, was finally detected by qRT-PCR and immunohistochemistry in CC tissues, and its expression correlates with miR-139-5p was explored.
Results: We found that miR-139-5p expression was frequently decreased in CC tissues and cell lines, and its lower level was associated with positive lymph node metastasis. Cellular assays proved the significant tumor-suppressing roles of miR-139-5p by inhibiting CC cell proliferation and migration, and markedly blocking Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Since bioinformatics analysis indicated TCF4 as a novel target of miR-139-5p, our mechanistic studies validated this, and confirmed that TCF4 restoration could attenuate the tumor inhibitory activities of miR-139-5p in CC progression, and recover the normal Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
Conclusion: Our data collectively demonstrated that miR-139-5p was a vital tumor suppressor in CC pathogenesis via targeting TCF4 thereby inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling. The miR-139-5p/TCF4 axis may serve as a promising target for CC therapy.
Keywords: cervical cancer, miR-139-5p, TCF4, Wnt/β-catenin signaling, tumor suppressor