110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

哥伦巴胺通过废除 Wnt/β-catenin 信号通路抑制结肠癌细胞的增殖和恶性生长
Authors Lei C, Yao Y, Shen B, Liu J, Pan Q, Liu N, Li L, Huang J, Long Z, Shao L
Received 24 March 2019
Accepted for publication 22 July 2019
Published 23 September 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 8635—8645
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S209861
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
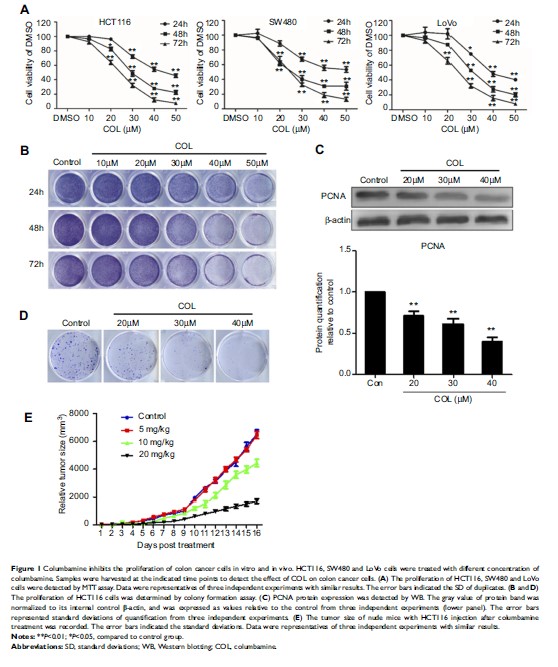
Background: Colon cancer is one of the most common malignancies worldwide. Because of the side effects and defects in tolerance of chemotherapy, it is necessary to discover new drugs for colon cancer treatment. Columbamine has been identified as an effective anti-osteosarcoma compound with only minor side effects. In this study, we analyzed the anticancer effect of columbamine on colon cancer.
Methods: Human colon cancer cell lines were treatment with columbamine. MTT assay, colony formation assay, apoptosis detection and tumorigenicity assay were performed to detect the protective effect of columbamine on colon cancer development. Western blot assay and luciferase reporter assay were conducted to investigate the potential mechanism of the columbamine treatment.
Results: Columbamine significantly inhibited the proliferation, migration, invasion process of colon cancer cells, and dramatically promoted the apoptosis rate of colon cancer cells to further suppress the development of colon cancer to tumor. Both the signaling transducing and key factors expression of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway were obviously repressed by columbamine treatment in a dose-dependent manner.
Conclusion: The present study indicated that columbamine exerts its anti-tumor effect in colon cancer cells through abolishing Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Columbamine may be a new therapy compound for colon cancer.
Keywords: colon cancer, cells growth, apoptosis, HCT116, LoVo