110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

抗菌肽鲎素抗菌肽 III 对多药耐药的绿脓杆菌(P. aeruginosa )和鲍曼不动杆菌(A. baumannii )共感染的动物模型的潜在作用
Authors Qi J, Gao R, Liu C, Shan B, Gao F, He J, Yuan M, Xie H, Jin S, Ma Y
Received 24 May 2019
Accepted for publication 24 August 2019
Published 23 September 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 2865—2874
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S217020
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Professor Suresh Antony
Background: Tachyplesin III , an antimicrobial peptide (AMP), provides protection against multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacterial infections and shows cytotoxicity to mammalian cells. Mixed bacterial infections, of which P. aeruginosa plus A. baumannii is the most common and dangerous combination, are critical contributors to the morbidity and mortality of long-term in-hospital respiratory medicine patients. Therefore, the development of effective therapeutic approaches to mixed bacterial infections is urgently needed.
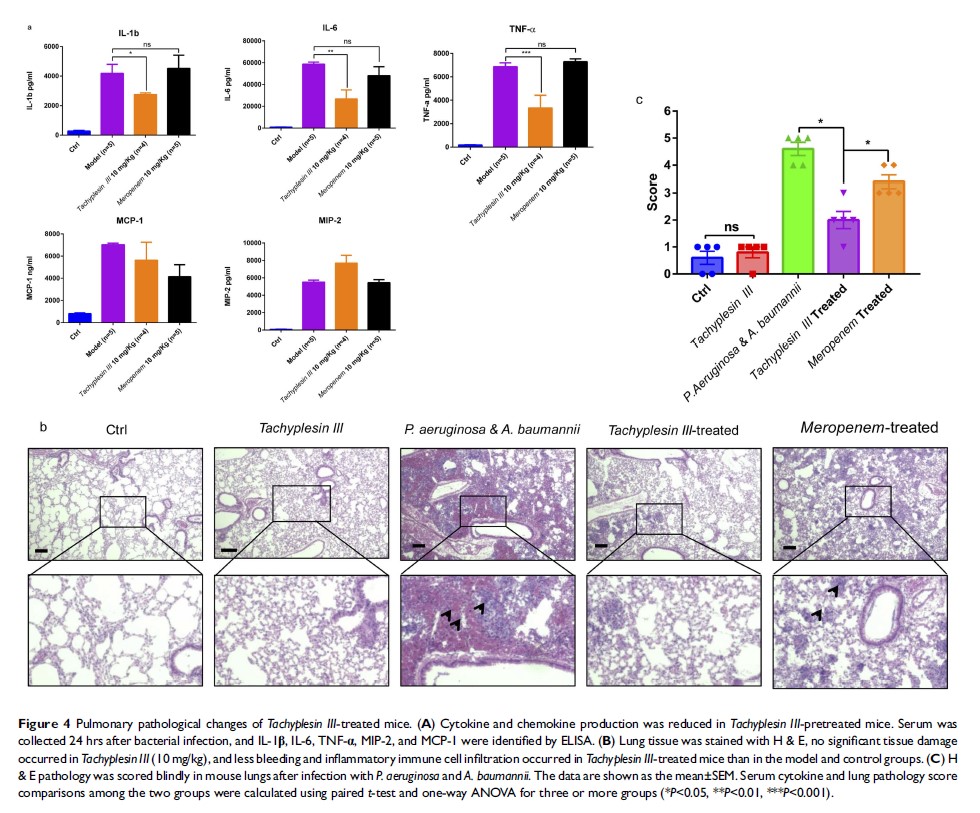
Methods and results: In this study, we demonstrated that compared with individual infections, mixed infections with MDR bacteria P. aeruginosa and A. baumannii cause more serious diseases, with increased pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α) and chemokines (MCP-1/MIP-2) and reduced mouse survival. In vitro treatment with Tachyplesin III enhanced phagocytosis in a mouse alveolar macrophage cell line (MH-S). Strikingly, in vivo, Tachyplesin III demonstrated a potential role against mixed-MDR bacterial coinfection. The bacterial burden in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) was significantly reduced in the Tachyplesin III -treated group. In addition, a systemic reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokines and decreased lung injury occurred with Tachyplesin III therapy.
Conclusion: Therefore, our study demonstrated that Tachyplesin III represents a potential therapeutic treatment against mixed-MDR bacterial infection in vivo, which sheds light on the development of therapeutic strategies against mixed-MDR bacterial infections.
Keywords: Tachyplesin III , antimicrobial peptides, multidrug-resistant bacterial, coinfection, phagocytosis