110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

TGF-β/Smad 通路抑制剂 SB431542 可增强射频消融对膀胱癌细胞的抗肿瘤作用
Authors Zhou HQ, Liu MS, Deng TB, Xie PB, Wang W, Shao T, Wu Y, Zhang P
Received 17 April 2019
Accepted for publication 9 September 2019
Published 23 September 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 7809—7821
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S212596
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Aruna Narula
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
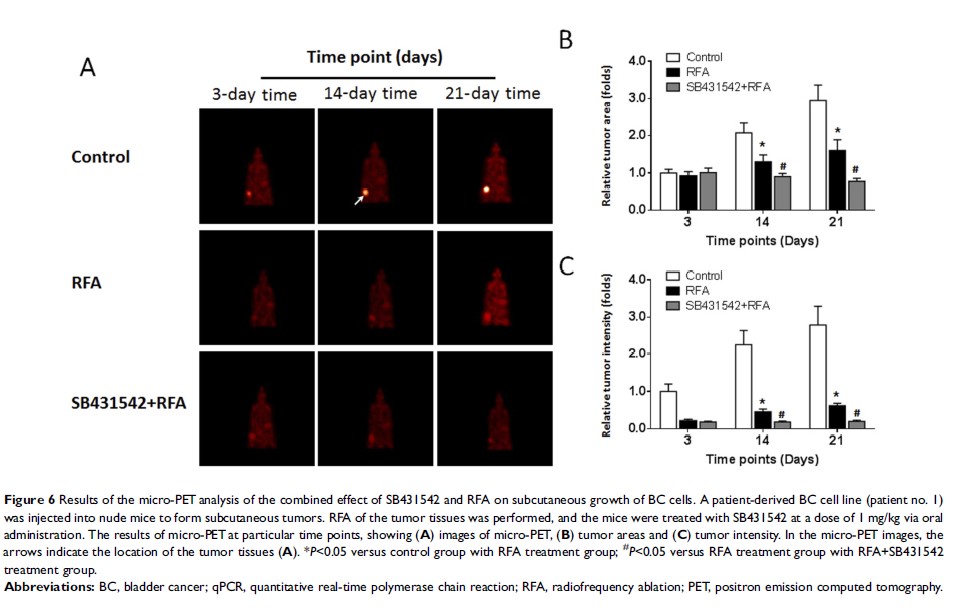
Background: Despite progress achieved in bladder cancer (BC) treatment, the prognosis of patients with advanced BC (ie, metastasized from the bladder to other organs) is poor. Although mortality in cases of low-grade BC is rare, the treatment, such as a radical cystectomy, often has a serious impact on the quality of life. Thus, research is needed to identify more effective treatment strategies and this work is aiming to examine the potential application of combination of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and SB435142, a inhibitor of transforming growth factor β (TGFβ)/Smad pathway.
Methods: BC cells were transplanted into nude mice (thymusdeficiency Bal B/c) to form subcutaneous tumors. The mice with subcutaneous tumors were then treated with RFA and oral administration of SB431542, an inhibitor of TGFβ/Smad signaling pathway. The antitumor effect of RFA was measured by tumor proliferation curves and micro-positron emission computed tomography (micro-PET). The effect of SB431542 on epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) related regulators in subcutaneous tumor tissues formed by BC cells were examined by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) experiments.
Results: The SB431542 treatment enhanced the antitumor effect of RFA on subcutaneous growth of BCs. SB431542 also decreased EMT-related regulators in subcutaneous tumor tissues formed by BC cells in nude mice.
Conclusion: SB431542 enhances the effect of RFA on BC.
Keywords: bladder cancer, radiofrequency ablation, SB431542, epithelial–mesenchymal transition