110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

治疗前炎症生物标记物可预测接受一线西妥昔单抗治疗加化疗的转移性结直肠癌患者的早期治疗反应和良好的生存率
Authors Jiang J, Ma T, Xi W, Yang C, Wu J, Zhou C, Wang N, Zhu Z, Zhang J
Received 3 April 2019
Accepted for publication 29 August 2019
Published 24 September 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 8657—8668
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S211089
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Melinda Thomas
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Bilikere Dwarakanath
Objective: This study was to determine whether peripheral blood biomarkers including neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and systemic immune inflammation index (SII) could predict early response to cetuximab; moreover, the prognostic ability of those biomarkers on progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) of metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) patients with wild-type (WT) RAS was also investigated.
Methods: mCRC patients with WT RAS treated with cetuximab plus chemotherapy were retrospectively analyzed, and early response was evaluated according to RECIST 1.1 after three or four treatment cycles. In prior to chemotherapy, hematologic data and clinic-pathological parameters were collected. The associations between pre-treatment inflammatory biomarkers and early response, and the prognostic value of those biomarkers were analyzed. A total of 102 patients were enrolled and divided into low or high NLR, PLR, and SII groups, respectively.
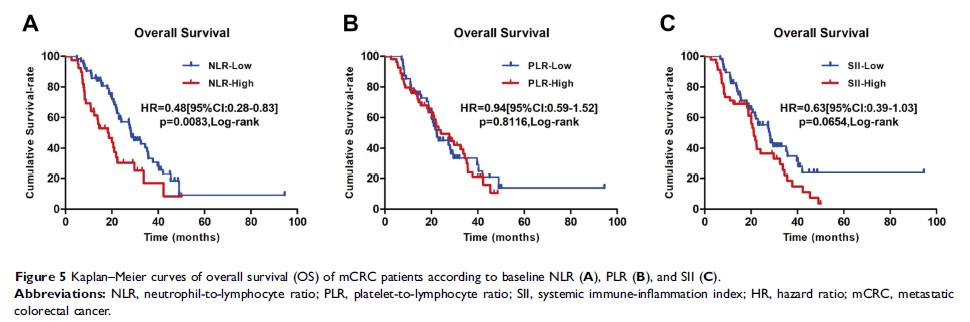
Results: The early response rate was significantly higher in the low NLR (p <0.001), low PLR (p =0.045), and low SII (p =0.011), respectively. In multivariate analyses, primary tumor resection (hazard ratio (HR) 0.411, p <0.001), carcino-embryonicantigen ≤5 ng/mL (HR 0.406, p <0.001), early treatment response (HR 0.322, p <0.001), and low NLR (HR 0.665, p =0.031) were independent factors of longer PFS. Primary tumor resection (HR 0.488, p =0.003) and early response (HR 0.392, p <0.001) were independent factors of longer OS. Further analysis showed that patients with early response, even in the high groups, can achieve better PFS and OS than non-responders.
Conclusion: Pre-treatment inflammatory biomarkers, especially NLR were predictors of benefit from cetuximab-combined therapy in mCRC patients. They were also predictors of significantly longer PFS and OS of early responders compared to non-responders.
Keywords: inflammatory biomarkers, cetuximab, early treatment response, wild-type RAS, metastatic colorectal cancer