110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA TUG1 介导的 KLF4 下调通过 miR-153-1 促进结直肠癌的转移和上皮向间充质转化
Authors Shao H, Dong D, Shao F
Received 12 March 2019
Accepted for publication 19 July 2019
Published 24 September 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 8699—8710
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S208508
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Nakshatri
Introduction: Taurine up-regulated 1 (TUG1) was reported to be over-expressed and involved in various human malignancies. However, its expression status and mechanistic importance in colorectal cancer (CRC) were yet to be defined.
Methods: Relative expressions of TUG1, miR-153-1 and Kruppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) were analyzed by real-time PCR. The potential influences of TUG1-proficiency and miR-153-1-deficiency on cell proliferation, migration and viability were determined by colony formation, wound healing and CCK-8 assays, respectively. Cell invasion was evaluated by transwell chamber assay. The regulatory effect of KLF4 on miR-153-1 was interrogated by luciferase reporter assay. Direct association between KLF4 and miR-153-1 promoter was measured by chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay. Subcellular localization of TUG1 was determined by fractionization PCR. Enrichment of EZH2 on KLF4 promoter was analyzed by ChIP-PCR. The pro-tumoral activity of TUG1 was determined using xenograft tumor model.
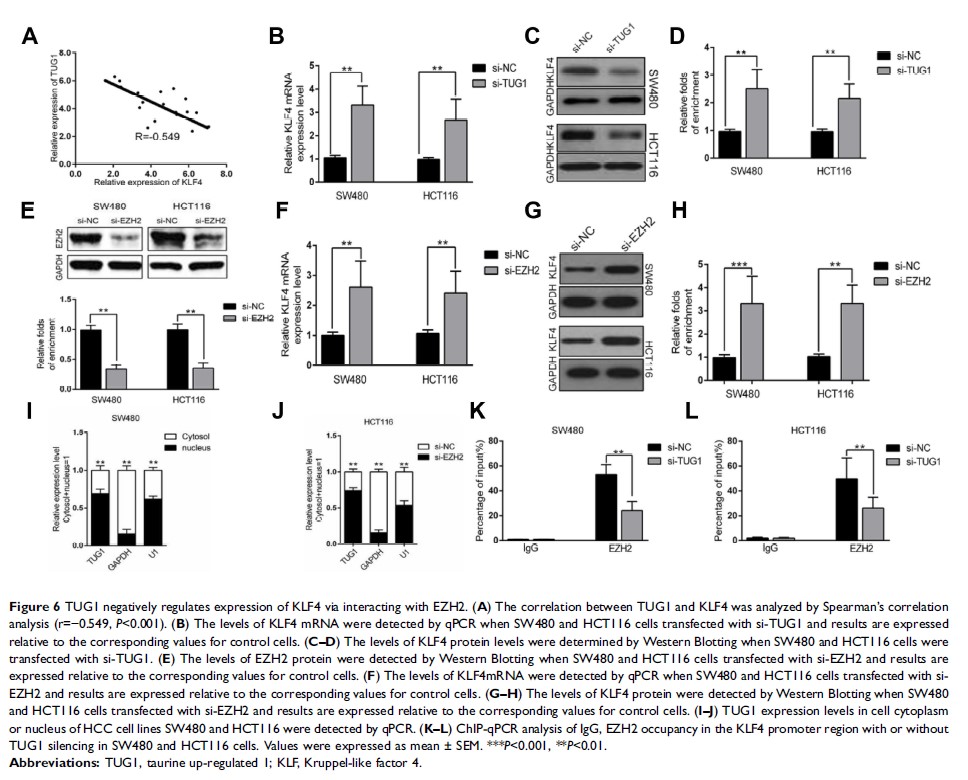
Results: We demonstrated the over-expression of TUG1 and down-regulation of miR-153-1 in CRC. Knockdown of TUG1 or ectopic over-expression of miR-153-1 in SW480 significantly suppressed cell proliferation, migration and viability. TUG1 negatively modulated miR-153-1 expression, and simultaneous expression of TUG1 completely abolished the anti-tumor effect of miR-153-1. We further identified KLF4 as a transcription factor of miR-153-1, which was negatively regulated by TUG1 along with EZH2.
Conclusion: Our study unravels the critical involvement of TUG1/KLF4/miR-153-1 axis in CRC.
Keywords: TUG1, miR-153-1, colorectal cancer, KLF4, EZH2