110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

在中国东部某大学医院流行的 bla NDM-5-阳性大肠杆菌的表征
Authors Sun P, Xia W, Liu G, Huang X, Tang C, Liu C, Xu Y, Ni F, Mei Y, Pan S
Received 31 July 2019
Accepted for publication 13 September 2019
Published 24 September 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 3029—3038
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S225546
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Joachim Wink
Purpose: The emergence and spread of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae deserves special concern worldwide. Unlike the epidemiological characteristics reported in other studies, we found that the production of New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase 5 was the main mechanism for the resistance of Escherichia coli to carbapenems.
Methods: All carbapenem-resistant strains were collected from July 2017 to July 2018 of the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University. The presence of carbapenemase-encoding genes was detected using PCR and gene sequencing. Genetic relatedness of the bla NDM-5-positive E. coli strains was determined with PFGE and MLST. Susceptibility profiles were measured with broth microdilution method and E-test strips. Transferability features of bla NDM-5 gene were assessed by conjugation experiments, S1-PFGE, southern blotting and PCR-based replicon typing methods. The genetic structures surrounding bla NDM-5 were acquired by whole genome sequencing and PCR mapping.
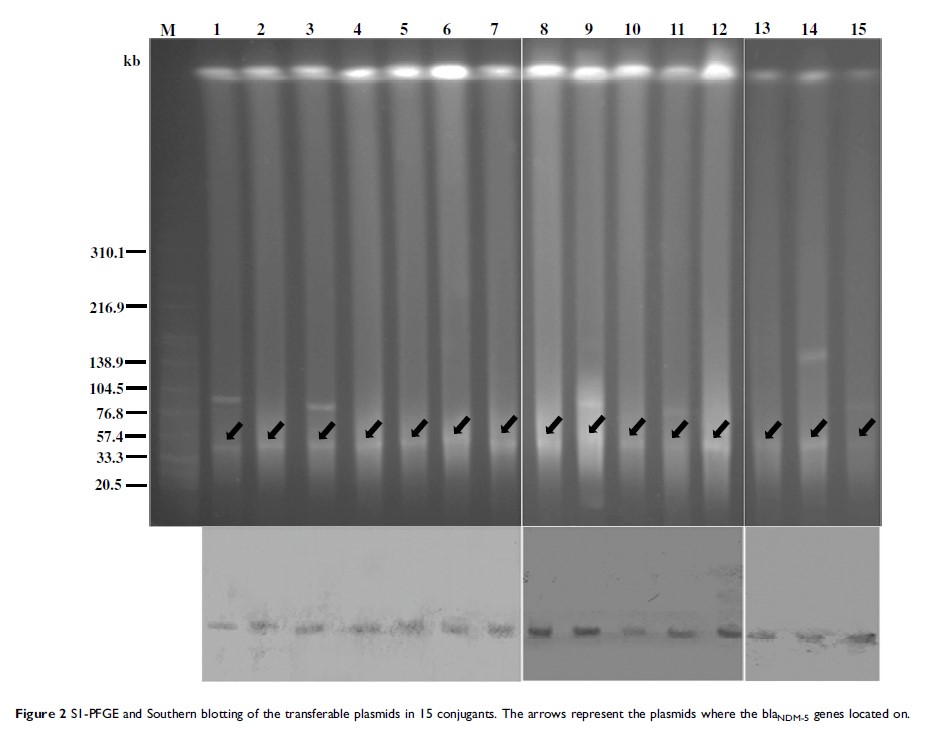
Results: Among the 28 carbapenem-resistant E. coli strains, 18 (64%) were verified as NDM-5 producers. The 18 bla NDM-5-positive E. coli strains showed high resistance to most antibiotics, but 100% were sensitive to colistin and tigecycline. In addition, the 18 bla NDM-5-positive E. coli strains belonged to eight STs, among which ST167, ST410 and ST101 were found to cause clonal spread in the hospital. Further studies found that the bla NDM-5 gene was located on an IncX3-type plasmid, and all plasmids harbored an IS3000-Δ ISAba125 -IS5-bla NDM-5-ble MBL-trpF-dsbC -IS26 structure.
Conclusion: The clonal spread of bla NDM-5-positive E. coli strains and horizontal dissemination via the pNDM-MGR 194-like plasmids should draw more attention. Appropriate infection control operations should be performed to prevent the further spread of bla NDM-5.
Keywords: Escherichia coli , carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae , New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase, bla NDM-5, IncX3 type plasmid