110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

类维生素 A X 受体选择性配体贝沙罗汀和多西他赛在前列腺癌中的协同作用
Authors Shen D, Wang H, Zheng Q, Cheng S, Xu L, Wang M, Li GH, Xia LQ
Received 21 March 2019
Accepted for publication 16 August 2019
Published 24 September 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 7877—7886
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S209307
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Shreya Arora
Peer reviewer comments 1
Editor who approved publication: Dr Gaetano Romano
Purpose: To explore if bexarotene (BEX) synergistically enhances docetaxel (DTX) cytotoxicity in castration-resistant prostate cancer cell lines.
Materials and methods: MTT assay was used to measure the cytotoxic effect of DTX and BEX on castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) cell proliferation and the combination index (CI) values calculated to analyze the interaction between DTX and BEX. Flow cytometry and Western blot analysis identified the underlying mechanism for the synergistic effect of BEX and DTX.
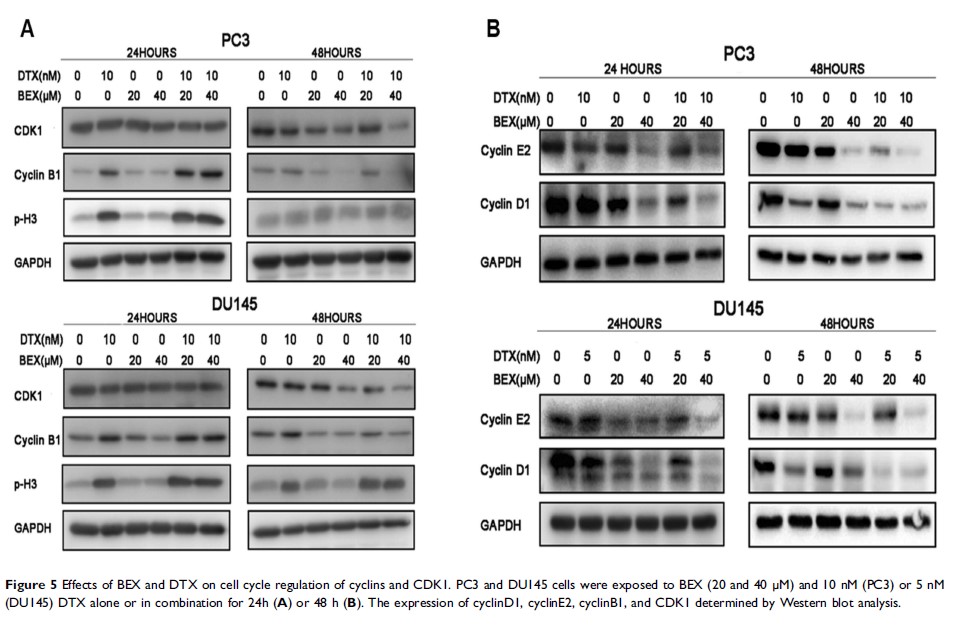
Results: When mitotic slippage happens, BEX can synergistically strengthen the anti-proliferation of DTX in a way of significantly down-regulating cyclinB1 and CDK1 expression, and then arresting cells in G2 phase.
Conclusion: Results from this study showed that BEX-induced G2 arrest and DTX-induced mitotic arrest probably contributed to the synergistic effect of BEX and DTX.
Keywords: docetaxel, bexarotene, prostate cancer, combination therapy, cell cycle arrest