110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

多变量 Logistic 回归和反向传播人工神经网络预测糖尿病性视网膜病变
Authors Yao L, Zhong Y, Wu J, Zhang G, Chen L, Guan P, Huang D, Liu L
Received 18 June 2019
Accepted for publication 16 September 2019
Published 25 September 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1943—1951
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S219842
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Nicola Ludin
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Konstantinos Tziomalos
Background: Monitoring and prediction of diabetic retinopathy (DR) is necessary in patients with diabetes for early discovery and timely treatment of disease. We aimed to analyze the association between DR and biochemical and metabolic parameters, and develop a predictive model for DR.
Methods: A total of 530 Chinese residents including 423 with type 2 diabetes (T2D) aged 18 years or older participated in this study. The association between DR and biochemical and metabolic parameters was analyzed by the univariate and multivariable logistic regression (MLR). According to the MLR results, we developed a back propagation artificial neural network (BP-ANN) model by selecting tan-sigmoid as the transfer function of the hidden layers nodes, and pure-line of the output layer nodes, with training goal of 0.5×10−5.
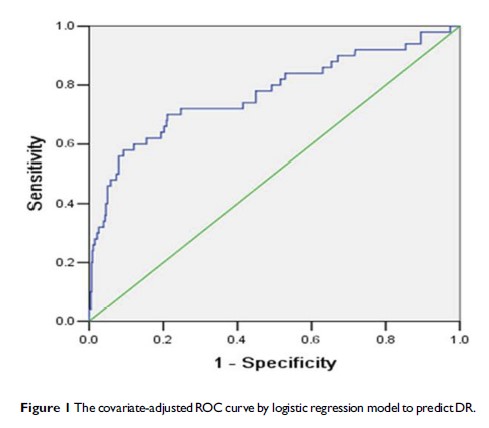
Results: There were 51 (9.6%) diabetic participants with DR. After univariate and MLR analysis, duration of diabetes, waist to hip ratio, HbA1c and family history of diabetes were independently associated with the presence of DR (all P < 0.05). Based on these parameters, the area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve for the BP-ANN model was significantly higher than that by MLR (0.84 vs. 0.77, P < 0.001).
Conclusion: Our evaluation demonstrated the potential role of BP-ANN model to identify DR in screening practice. The presence of DR was well predictable using the proposed BP-ANN model based on four related parameters (duration of diabetes, waist to hip ratio, HbA1c and family history of diabetes).
Keywords: diabetic retinopathy, type 2 diabetes, regression, BP-ANN