110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

BMP7 在卵巢癌中的表达及其对小鼠卵巢癌细胞的生物学效应
Authors Guan H, Li J, Sun R, Liu W, Feng M, Ma H, Li C
Received 1 June 2019
Accepted for publication 6 September 2019
Published 26 September 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 7897—7909
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S217975
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Aruna Narula
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tohru Yamada
Purpose: The aim of our research was to investigate the expression of BMP7 in ovarian cancer (OC) and the biological effect of knocking down BMP7 on ovarian cancer A2780 cells.
Methods: We detected BMP7 expression in ovarian cancer and normal ovarian tissue by immunohistochemistry (IHC). We downregulated BMP7 expression using lentivirus-mediated RNAi and then examined the effects of knocking down BMP7 on the cell growth and invasion, cell cycle and paclitaxel sensitivity of A2780 cells. The mRNA and protein levels were detected by total RNA extraction and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and Western blotting, respectively. Cell proliferation was measured by CCK-8 and colony formation assays. The number of cells in each cell cycle stage and those undergoing apoptosis were measured by flow cytometry.
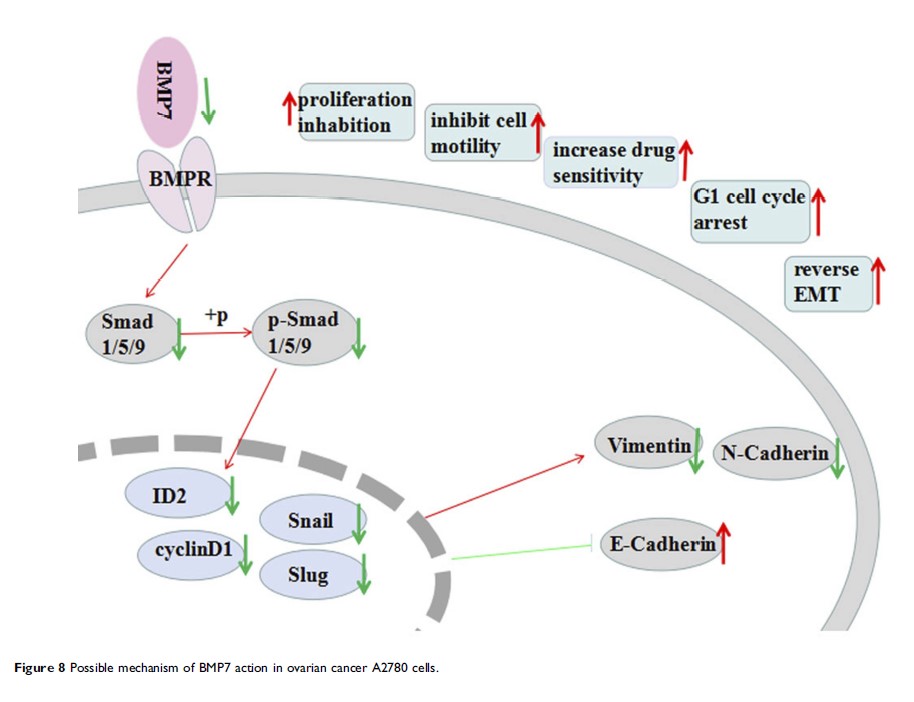
Results: BMP7 expression was significantly higher in the ovarian cancer tissues than it was in the normal ovarian tissues. Knocking down BMP7 in ovarian cancer A2780 cells inhibited cell proliferation, migration and invasion; led to G1 cell cycle arrest; and reversed the epithelial-mesenchymal transformation (EMT) process. In addition, downregulating BMP7 increased the sensitivity of the A2780 cells to paclitaxel. Moreover, BMP7 downregulation resulted in decreased expression of Smad1/5/9, p-Smad1/5/9, ID2 and cyclin D1 protein.
Conclusion: The results presented here are expected to contribute to the development of possible therapeutic targets for patients with ovarian cancer.
Keywords: BMP7, ovarian cancer, EMT, drug sensitivity, proliferation, cell cycle