110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

使用二氧化硅涂层磁铁矿纳米粒子改善钆螯合物的纵向横向弛豫
Authors Xu K, Liu H, Zhang J, Tong H, Zhao Z, Zhang W
Received 12 April 2019
Accepted for publication 6 September 2019
Published 26 September 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 7879—7889
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S211974
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Melinda Thomas
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Introduction and objective: Precisely and sensitively diagnosing diseases especially early and accurate tumor diagnosis in clinical magnetic resonance (MR) scanner is a highly demanding but challenging task. Gadolinium (Gd) chelate is the most common T 1 magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agent at present. However, traditional Gd-chelates are suffering from low relaxivity, which hampers its application in clinical diagnosis. Currently, the development of nano-sized Gd based T 1 contrast agent, such as incorporating gadolinium chelate into nanocarriers, is an attractive and feasible strategy to enhance the T 1 contrast capacity of Gd chelate. The objective of this study is to improve the T 1 contrast ability of Gd-chelate by synthesizing nanoparticles (NPs) for accurate and early diagnosis in clinical diseases.
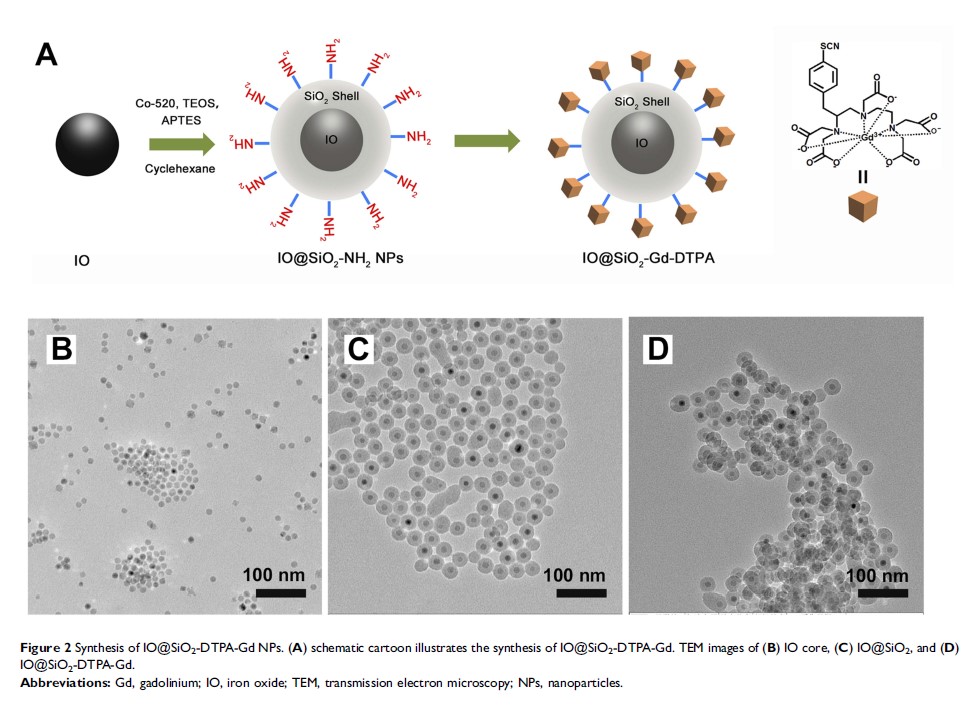
Methods: Reverse microemulsion method was used to coat iron oxide (IO) with tunable silica shell and form cores of NPs IO@SiO2 at step one, then Gd-chelate was loaded on the surface of silica-coated iron oxide NPs. Finally, Gd-based silica coating magnetite NPs IO@SiO2-DTPA-Gd was developed and tested the ability to detect tumor cells on the cellular and in vivo level.
Results: The r 1 value of IO@SiO2-DTPA-Gd NPs with the silica shell thickness of 12 nm was about 33.6 mM−1s−1, which was approximately 6 times higher than Gd-DTPA, and based on its high T 1 contrast ability, IO@SiO2-DTPA-Gd NPs could effectively detect tumor cells on the cellular and in vivo level.
Conclusion: Our findings revealed the improvement of T 1 relaxation was not only because of the increase of molecular tumbling time caused by the IO@SiO2 nanocarrier but also the generated magnetic field caused by the IO core. This nanostructure with high T 1 contrast ability may open a new approach to construct high-performance T 1 contrast agent.
Keywords: gadolinium chelate, silica, iron oxide, nanoparticles, T 1 relaxivity, tumbling time