110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

TCF-4 调控下的 lncRNA-XIST 可促进 M2 型巨噬细胞极化,并与肺癌相关
Received 2 April 2019
Accepted for publication 3 September 2019
Published 2 October 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 8055—8062
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S210952
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Aruna Narula
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
Background: Little is known about the biological function of long non-coding RNA X inactive specific transcript (lncRNA XIST) and its underlying mechanism in tumor-associated macrophage (TAM) polarization of lung cancer.
Materials and methods: The expression of lncRNA XIST in macrophages was detected by RT-qPCR. The function of lncRNA XIST on IL-4-induced M2 polarization was evaluated by transfection of shRNA and RT-qPCR or Western blotting detection of M2 specific markers. Contact between T-cell-specific transcription factor 4 (TCF-4) and lncRNA XIST was verified by bioinformatics and luciferase assay. The relation between lncRNA XIST and lung cancer was determined by bioinformatics.
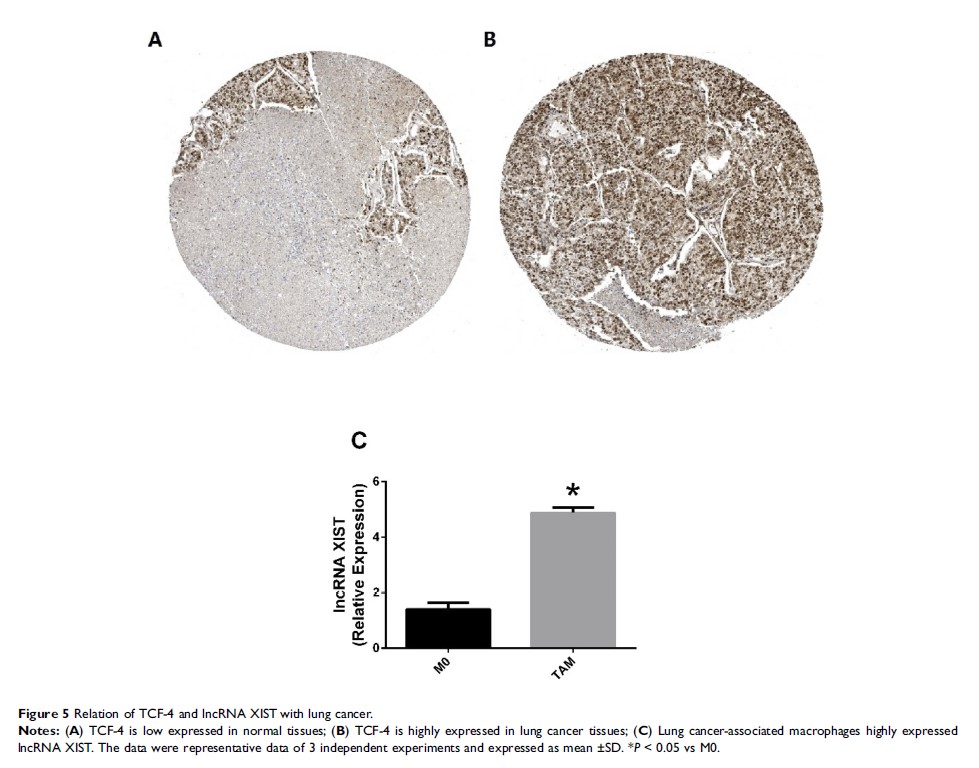
Results: The expression of lncRNA XIST in THP-1-differentiated macrophages was significantly increased in M2 macrophages than M1 (P < 0.05). lncRNA XIST downregulation suppressed the IL-4-induced M2 polarization, inducing downregulation of M2 specific markers such as IL-10, Arg-1, and CD163. However, the suppression was aborted by overexpression of TCF-4. Mechanistically, lncRNA XIST was regulated by TCF-4 through direct binding. Additionally, lung cancer conditioned macrophages exhibited high expression of lncRNA XIST and lung cancer tissues highly expressed TCF-4, indicating TCF-4 regulated lncRNA XIST closely correlated with macrophage polarization and tumor progression of lung cancer.
Conclusion: Taken together, this study demonstrated the important role of TCF-4 regulated lncRNA XIST in regulating M2 polarization and gave a novel insight into the TAMs regulation and potential therapeutic target of lung cancer.
Keywords: lncRNA, XIST, TCF-4, lung cancer