110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

癌症中癌细胞和淋巴管的联系:侧重于膀胱癌
Authors Wu Z, Ding W, Cai J, Bashir G, Li Y, Wu S
Received 11 June 2019
Accepted for publication 7 August 2019
Published 3 October 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 8161—8177
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S219111
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Shreya Arora
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Gaetano Romano
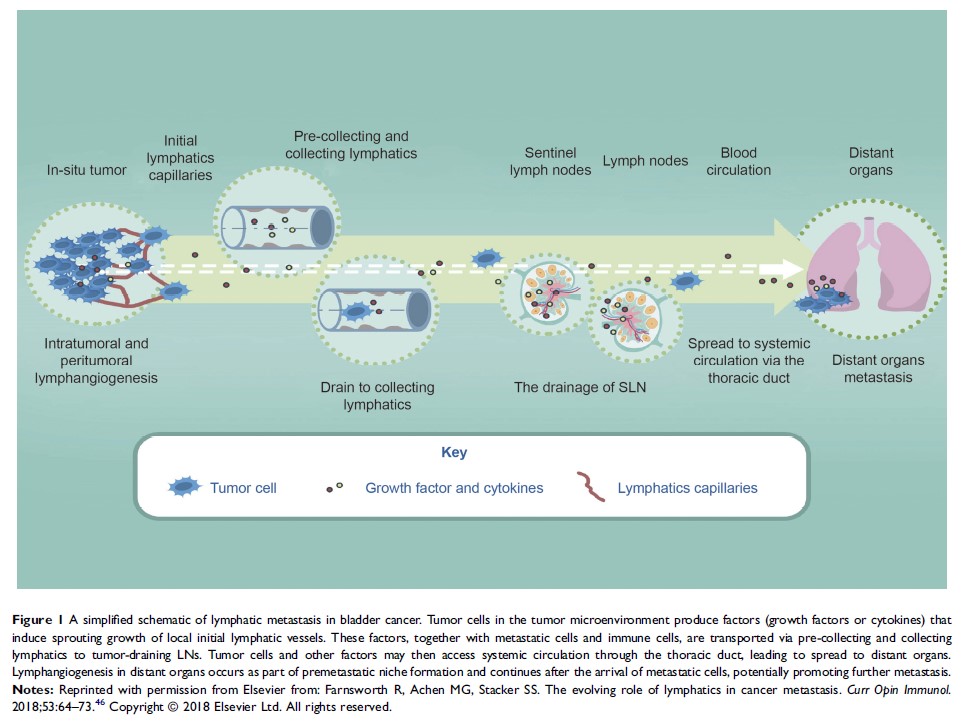
Abstract: Bladder cancer is one of the most commonly diagnosed cancers worldwide and causes the highest lifetime treatment costs per patient. Bladder cancer is most likely to metastasize through lymphatic ducts, and once the lymph nodes are involved, the prognosis is poorly and finitely improved by current modalities. The underlying metastatic mechanism for bladder cancer is thus becoming a research focus to date. To identify relevant published data, an online search of the PubMed/Medline archives was performed to locate original articles and review articles regarding lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis in urinary bladder cancer (UBC), and was limited to articles in English published between 1998 and 2018. A further search of the clinical trials.gov search engine was conducted to identify both trials with results available and those with results not yet available. Herein, we summarized the unique mechanisms and biomarkers involved in the malignant progression of bladder cancer as well as their emerging roles in therapeutics, and that current data suggests that lymphangiogenesis and lymph node invasion are important prognostic factors for UBC. The growing knowledge about their roles in bladder cancers provides the basis for novel therapeutic strategies. In addition, more basic and clinical research needs to be conducted in order to identify further accurate predictive molecules and relevant mechanisms.
Keywords: bladder cancer, lymphangiogenesis, lymphatic metastasis, biomarkers, tumor progression, treatment