108899
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

本文章已被撤回:CXCL8 通过激活 JAK/STAT1/HIF-1α/Snail 信号转导轴来促进神经胶质瘤进展
Authors Chen Z, Mou L, Pan Y, Feng C, Zhang J, Li J
Received 25 July 2019
Accepted for publication 12 September 2019
Published 3 October 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 8125—8138
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S224721
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Rachel Predeepa
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
***本文章已被撤回***
Background: Upregulation of CXCL8 (C-X-C motif ligand 8) in tumor cells has been reported in several types of cancer, and it correlates with a poor prognosis. However, the role of CXCL8 in glioma progression remains unknown.
Materials and methods: In this study, we examined CXCL8 expression levels in human glioma cell lines and in sixteen human gliomas with different grades. The molecular role of CXCL8 in glioma cells was investigated using quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) assays, Western blotting, CCK-8 assays, EdU assays, colony formation assays, Transwell migration and invasion assays.
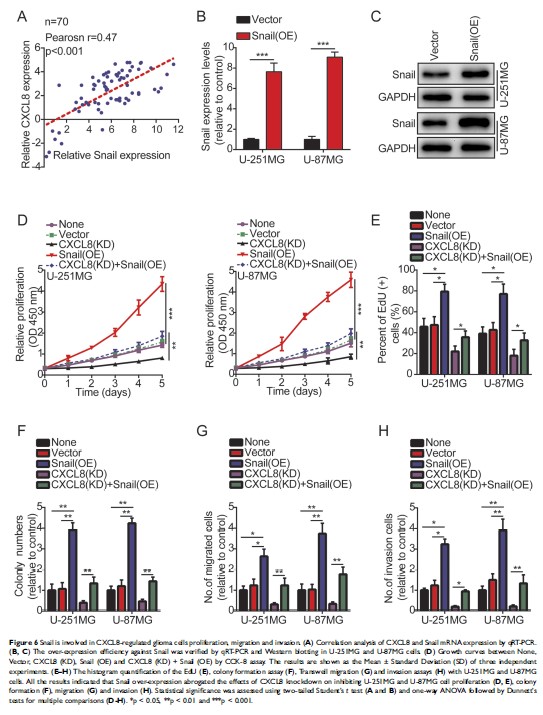
Results: We found that high expression levels of CXCL8 were positively associated with progression and poor prognosis in human glioma. Mechanistically, CXCL8 promoted the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in glioma cells by activating the JAK/STAT1/HIF-1α/Snail signaling pathway.
Conclusion: Taken together, our data provide a plausible mechanism for CXCL8-modulated glioma progression, which suggests that CXCL8 may represent a potential therapeutic target in the prevention and treatment of gliomas.
Keywords: glioma, progression, CXCL8, JAK/STAT1/HIF-1α/Snail