110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

circZNF609 通过使 miR-483-3p 海绵化并调节 CDK6 来促进胃癌的增殖和迁移
Authors Wu W, Wei N, Shao G, Jiang C, Zhang S, Wang L
Received 1 November 2018
Accepted for publication 21 May 2019
Published 4 October 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 8197—8205
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S193031
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
Objective: To explore the regulatory effects of circZNF609 on proliferative and migratory capacities of gastric cancer (GC) and its underlying mechanism.
Methods: Expression level of circZNF609, CDK6 and miR-483-3p in GC tissues and cells were detected qRT-PCR verification. CCK-8 and transwell assay were conducted the cell viability and migratory capacities of GC cells. Dual luciferase assay was enrolled to confirm the interaction among circZNF609, CDK6 and miR-483-3p. Western blot was used to detect the protein level of CDK6.
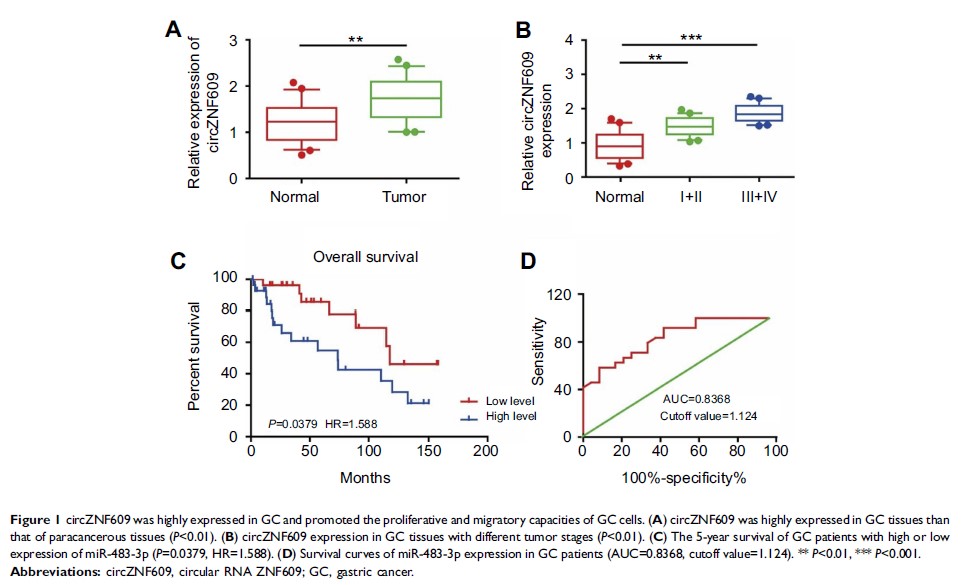
Results: Expression levels of circZNF609 were higher in GC patients by qRT-PCR.GC patients with higher expression of circZNF609 were expected to have a higher TNM stage and lower 5-year survival than those with lower expression. ROC curves showed a well diagnostic value of circZNF609 in GC. Treatment of RNase R in GC cells downregulated the expression of ZNF609, whereas circZNF609 expression did not change. Furthermore, cytoplasmic expression of circZNF609 was higher than those of nuclear expression. Besides, biological experiments indicated that overexpression of circZNF609 promoted the proliferative and migratory capacities of GC cells. To demonstrate the underlying mechanism of circZNF609, we found that circZNF609 bound to miR-483-3p, which presented a lower expression in GC tissues than that of paracancerous tissues. Both circZNF609 and miR-483-3p could bind to Ago2, suggesting that circZNF609 may act as a sponge of miR-483-3p. In addition, the effect of overexpressed circZNF609 on cellular behaviors of GC cells were partly reversed by overexpression of miR-483-3p. Bioinformatics suggested that CDK6 has a potential binding site with miR-483-3p. The expression of CDK6 markedly increased in GC tissues and cells, which was negatively correlated with miR-483-3p expression. Dual-luciferase reporter gene results indicated that miR-483-3p could bind to the 3’-UTR of CDK6. Moreover, miR-483-3p downregulated CDK6 at both mRNA and protein levels. Overexpression of miR-483-3p inhibited proliferative and migratory capacities of GC cells, which were reversed by CDK6 overexpression.
Conclusion: In summary, the expression of circZNF609 is upregulated in GC. CircZNF609 can be used as the sponge of miR-483-3p to regulate the expression level of CDK6, thus participating in the progression of GC by regulating the proliferative and migratory capacities of GC cells.
Keywords: circZNF609, MiR-483-3p, CDK6, proliferation, migration, gastric cancer