110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

单独使用阿帕替尼或阿帕替尼联合化学疗法治疗复发/晚期卵巢癌患者的疗效和安全性研究
Authors Yang M, Liu X, Zhang C, Liao F, Li Z, Luo X, Sun Y, Chen C
Received 16 July 2019
Accepted for publication 23 September 2019
Published 9 October 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 8869—8876
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S223372
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Mr Davin Leif
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eileen O'Reilly
Objectives: Despite recent advances in the treatment of advanced ovarian cancer, drug selection after second-line chemotherapy has not been well studied. In this study, we retrospectively evaluated the effect and safety of apatinib as monotherapy or in combination with chemotherapy for the treatment of advanced ovarian cancer after second-line treatment.
Methods: We reviewed the medical records of patients from April 2016 to October 2018 with advanced ovarian cancer who received apatinib after failed second-line chemotherapy. Overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) were calculated by the Kaplan–Meier method. Response rate (RR) and disease control rate (DCR) were evaluated using radiologic reports according to RECIST 1.1 criteria. Treatment-related adverse events were evaluated based on NCI-CTC version 4.0.
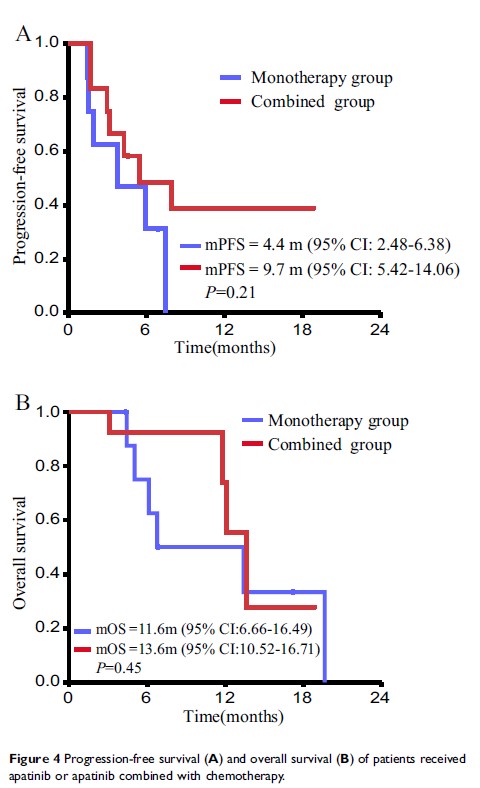
Results: Study concerned 22 evaluated cases; of them, 13 patients received apatinib combined with chemotherapy and 9 patients received apatinib monotherapy. The median PFS was 8.2 months (9.7 months in combined group and 4.4 months in monotherapy group, P value was 0.21). The median OS was 13.1 months (13.6 months in combined group and 11.6 months in monotherapy group, P value was 0.45). The RR was 20% and DCR was 85% (combined group: RR 33.3%, DCR 100%, monotherapy group: RR 0%, DCR 62.5%). The main side effect was hypertension (9/22), proteinuria (7/22), oral mucositis (5/22), hand and foot syndrome (6/22%), leukopenia (5/22), etc.
Conclusion: Apatinib showed good efficacy and safety for advanced ovarian cancer patients whether used alone or in combination with chemotherapy. In the meanwhile, this study is limited by the small cases number. Therefore, further research is needed to provide more data and ultimately apply it to guide clinical practice.
Keywords: apatinib, chemotherapy, ovarian cancer, efficacy and safety