111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

使用生物信息学分析,五个中枢基因可能是胆管癌的潜在 DNA 甲基化生物标志物
Authors Chen D, Wu H, He B, Lu Y, Wu W, Liu H, Feng X, Chen J, Wu J
Received 29 January 2019
Accepted for publication 20 September 2019
Published 11 October 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 8355—8365
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S203342
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Aruna Narula
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
Background: Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is a subtype of highly malignant hepatic tumor, which has low 5-year survival rate and poor clinical outcome. Only a few patients can be detected early and accepted with the surgery. Most of CCA patients are diagnosed in advanced stage, and the treatments are limited. As for the inoperable, advanced CCA patients, chemotherapy is the main treatment, due to lacking molecular targets, therapeutic effect is limited.
Materials and methods: To explore potential therapeutic targets for CCA, we analyzed three microarray datasets derived from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. Then, we used GEO2R tools of NCBI to discover the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) from the CCA and normal liver tumor microarrays (TMA). Subsequently, we used the Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery (DAVID GO) to perform the Gene Ontology function (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis. Then, we carried out the Cytoscape software to search for the hub genes downregulated in CCA and identify the protein–protein interaction (PPI) of these genes. Besides, we used the GEPIA tool to evaluate the differential expressions of hub genes in CCA patients. Then, we also used MEXPRESS database to detect the promoter methylation levels of hub genes in CCA and normal tissue samples. In addition, we evaluated the expression of these genes in CCA lines and normal bile tract cells after 5-AZA (DNA methyltransferase inhibitor) treatment.
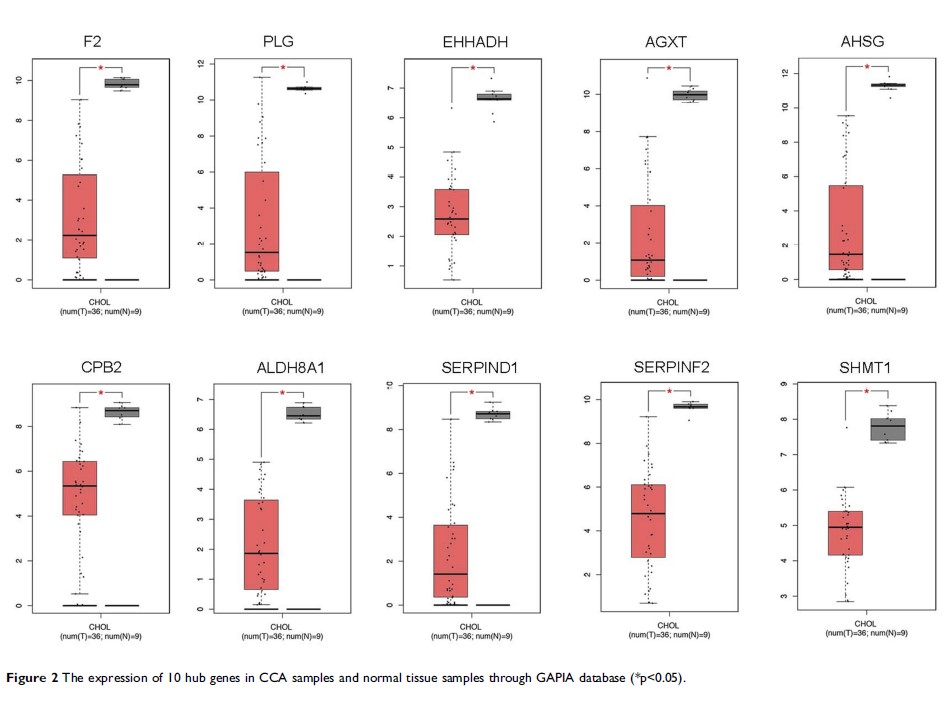
Results: A total of 115 downregulated DEGs were identified. Among them, 10 hub genes with a high degree of connectivity were picked out. Among these 10 hub genes, F2, AHSG, ALDH8A1, SERPIND1 and AGXT showed higher DNA methylation levels of promoter in CCA compared with normal liver tissues. Therefore, these 5 genes may be the potential DNA methylation biomarkers and therapeutic targets in CCA.
Keywords: cholangiocarcinoma, hub genes, expression profiling data, methylation