111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

肾脏 GLUT2 和 SGLT2 的上调与小鼠高脂饮食诱发的妊娠糖尿病有关
Authors Jiang YK, Xin KY, Ge HW, Kong FJ, Zhao G
Received 30 June 2019
Accepted for publication 13 September 2019
Published 14 October 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 2095—2105
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S221396
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Melinda Thomas
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Ming-Hui Zou
Introduction: Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a metabolic disorder during mid- to late-pregnancy characterized by hyperglycemia, insulin resistance and fetal mal-development. Glucose transporter type 2 (GLUT2) and sodium-coupled glucose cotransporters 2 (SGLT2) in the proximal tubules play a critical role in the reabsorption of glucose and have been linked to the occurrence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Our study was designed to investigate the role of GLUT2 and SGLT2 in the pathogenesis of GDM, which is considered a forerunner of T2DM, and investigate the related molecular mechanism.
Methods: High-fat diet (HFD) was utilized to build a GDM mouse model that closely induces metabolic abnormalities similar to human GDM. Body weight, blood glucose and serum insulin were recorded in the experimental process. Glucose tolerance was determined by the use of an intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (IPGTT). In addition, levels of GLUT2 and SGLT2 were evaluated to further explore the underlying mechanism of GDM.
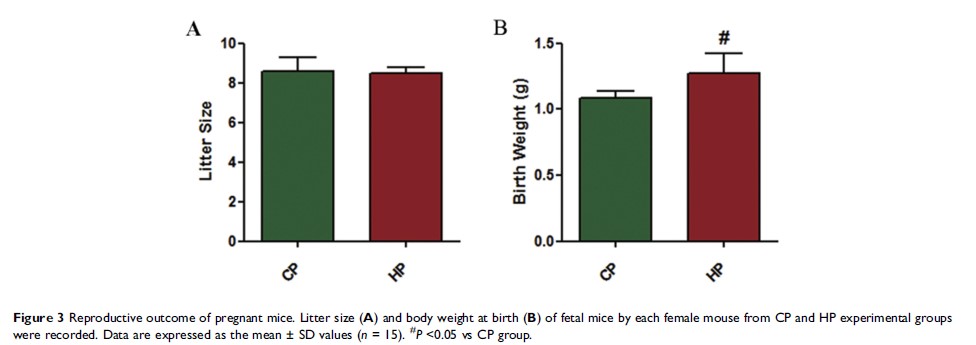
Results: HFD feeding induced abnormal glucose metabolism as manifested by increased levels of blood glucose and insulin and prominent glucose intolerance. Additionally, fetal mice from mother feed on HFD showed higher mean body weight. Furthermore, HFD feeding led to an increase in the number of positive cells of GLUT2 and SGLT2 in the renal proximal tubule and the expressions of renal GLUT2 and SGLT2 mRNA and proteins in mice. However, no obvious change was observed in renal morphology.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrates a potential involvement of renal GLUT2 and SGLT2 in GDM pathology in an HFD-induced GDM mouse model, which further supports the role of renal GLUT2 and SGLT2 not only in T1DM and T2DM but also in GDM.
Keywords: gestational diabetes mellitus, insulin resistance, renal threshold for glucose, GLUT2, SGLT2