111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过靶向 PI3K/Akt 信号通路来遏制 ROS 原癌基因 1,从而抑制胃癌细胞的迁移和侵袭
Authors Qiao J, Li M, Sun D, Li W, Xin Y
Received 26 April 2019
Accepted for publication 24 July 2019
Published 16 October 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 8569—8582
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S213421
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Shreya Arora
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
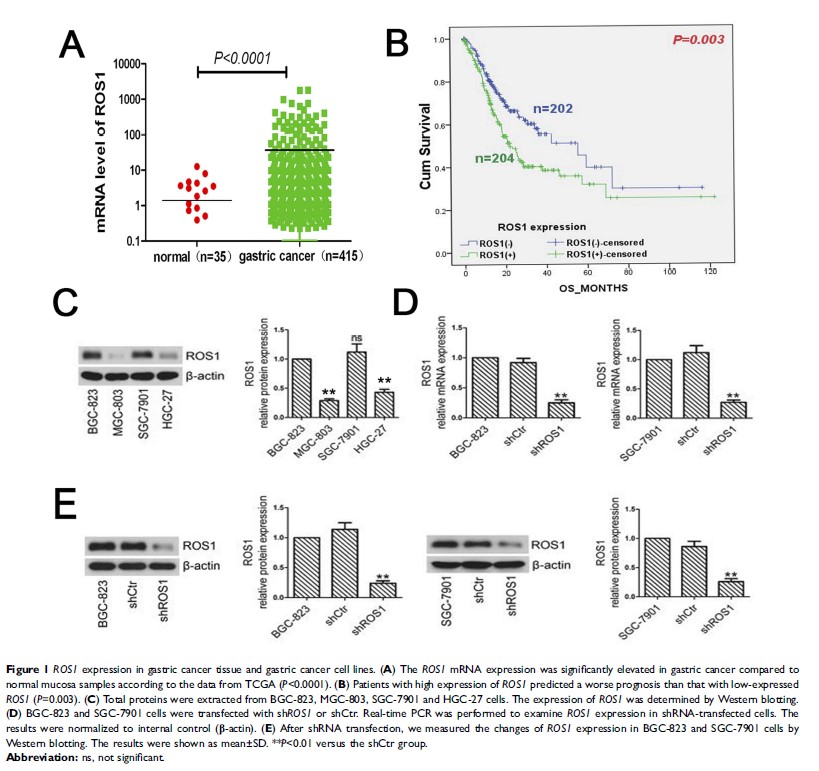
Objectives: Gastric cancer ranks the fourth most common cancer and the third leading cause of cancer mortality in the world. ROS proto-oncogene 1 (ROS1 ) is an oncogene and ROS1 rearrangement has been reported in many cancers. Our study aimed to investigate the potential function and the precise mechanisms of ROS1 in gastric cancer.
Methods: In our study, the analysis of ROS1 expression and clinical pathologic factors of gastric cancer in gastric cancer using TCGA database demonstrated that ROS1 expression was elevated in gastric cancer and related to T, N, M and TNM staging. High expression of ROS1 predicted poor survival in patients with gastric cancer. Then, we measured ROS1 expression in four human gastric cancer cell lines and knocked down ROS1 expression in BGC-823 and SGC-7901 cells by specific shRNA transfection via Lipofectamine 2000. The effect of ROS1 knockdown on cell proliferation, cell cycle distribution, cell apoptosis and metastasis in vitro was evaluated by MTT, colony formation, flow cytometric analysis, wound healing and Transwell invasion assays. The levels of apoptosis-related proteins, EMT markers and the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway members were measured by Western blotting.
Results: We demonstrated that shROS1 transfection markedly downregulated ROS1 expression in BGC-823 and SGC-7901 cells. Knockdown of ROS1 inhibited cell survival, clonogenic growth, migration, invasion and epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), as well as induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in gastric cancer cells. Furthermore, ROS1 knockdown inhibited the phosphorylation of PI3K and Akt.
Conclusion: Collectively, our data suggest that ROS1 may serve as a promising therapeutic target in gastric cancer treatment.
Keywords: gastric cancer, ROS1 , shRNA, proliferation, apoptosis, metastasis, EMT