111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

MiR-4766-5p 通过靶向 NKAP 抑制胃癌的发展和进展
Authors Wei Y, Wang Y, Zang A, Wang Z, Fang G, Hong D
Received 20 June 2019
Accepted for publication 16 September 2019
Published 16 October 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 8525—8536
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S220234
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Aruna Narula
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
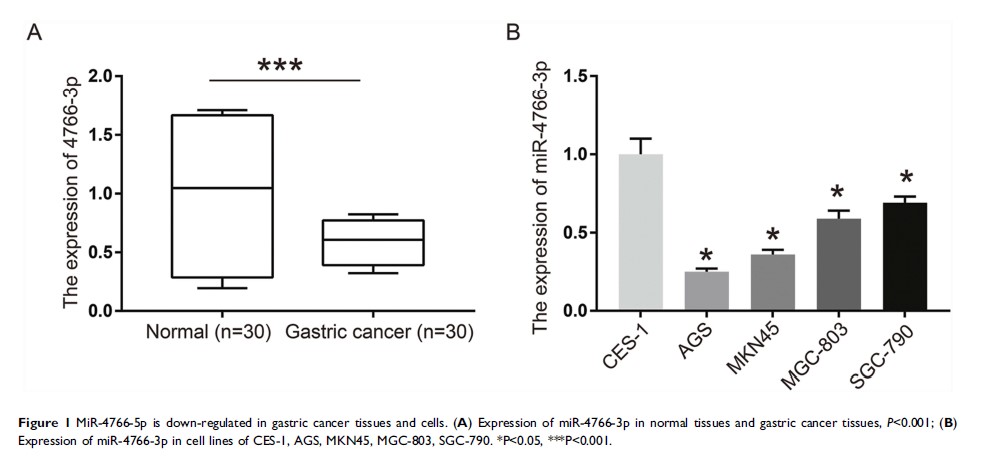
Purpose: It is widely known that some specific microRNAs can regulate the expressions of genes in gastric cancer cells at the post-transcriptional level. Previous studies have identified that miRNA-4766-5p was involved in tumor cell proliferation and can be an independent prognostic indicator for malignant pleural mesothelioma. However, the mechanism underlying gastric cancer via the miRNA-4766-5p pathway remains to be blank.
Methods: We investigated the expression of miR-4766-5p in gastric cancer tissues and cells through qRT-PCR. We used RNAi to change the expressions of miR-4766-5p in gastric cancer cell lines, AGS and MKN45. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was employed to detect the mRNA expression of miR-4766-5p. We identified cell proliferation by CCK8 and clone formation assays. We analyzed the cell apoptosis and cycle through flow cytometry. At last, we used a dual-luciferase reporter assay to illustrate the interaction between miR-4766-5p and NKAP and used Western blot to determine the protein expression of signaling pathways.
Results: We found that 1) miR-4766-5p was down-regulated in gastric cancer tissues and cells lines; 2) miR-4766-5p inhibited cell proliferation of gastric cancer cell lines significantly; 3) miR-4766-5p significantly inhibited cell migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells; 4) miR-4766-5p induced gastric cancer cell apoptosis. 5) NKAP was a direct target gene of miR-4766-5p; and 6) miR-4766-5p induced inactivation of AKT/mTOR pathway.
Conclusion: The above results indicate that miR-4766-5p suppressed the proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer cells through targeting NKAP. Our findings could probably contribute to the diagnostics and prognostics of gastric cancer through new methodologies.
Keywords: miR-4766-5p, progression, gastric cancer, NKAP