111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

环状 RNA circ-Foxo3 通过与 miR-191-5p 相互作用诱导尿路上皮癌细胞凋亡
Authors Wang C, Tao W, Ni S, Chen Q
Received 15 May 2019
Accepted for publication 4 August 2019
Published 16 October 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 8085—8094
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S215823
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aok
Background: Circular RNAs (circRNAs) play a critical role in cancer. Emerging evidence has shown circ-Foxo3, a circRNA, was dysregulated in a variety of tumor types. However, the exact role of circ-Foxo3 in bladder cancer has never been studied.
Methods: We measured the expression level of circ-Foxo3 in human and murine bladder cancer tissues and in various human bladder cancer cell lines. We induced bladder cancer in mice by a carcinogen N-butyl-N-(4-hydroxybutyl)nitrosamine (BBN). circ-Foxo3 was overexpressed in mice by lentiviral gene transfer and in cultured cells via overexpression plasmid. The effect of circ-Foxo3 on apoptosis was examined via apoptotic marker staining, Western blot, and flow cytometry. We further characterized the interaction between circ-Foxo3 and miR-191 and its functional impact on bladder cancer cells.
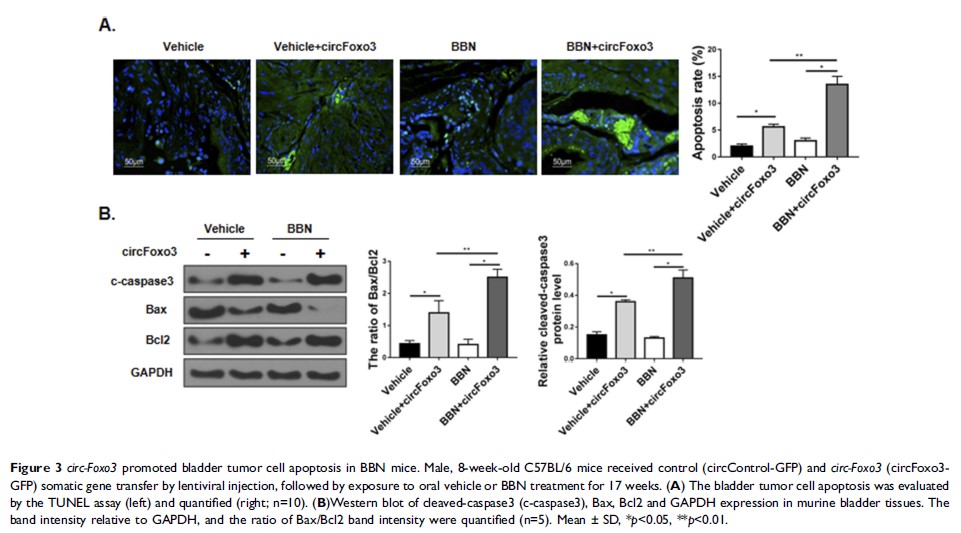
Results: circ-Foxo3 was downregulated in bladder cancer in vivo and in vitro, and was upregulated in response to apoptotic stress. Overexpression of circ-Foxo3 promoted bladder cancer cell apoptosis in BBN mice and in human bladder cancer cell lines. miR-191-5p suppressed circ-Foxo3 expression and the pro-apoptotic effect of circ-Foxo3 in bladder cancer cells via directly targeting the 3ʹ-untranslated region (3ʹ-UTR) of circ-Foxo3 .
Conclusion: circ-Foxo3 was downregulated in bladder cancer in vivo and in vitro, and promoted bladder cancer apoptosis via direct interaction with miR-191. circ-Foxo3 could be a potential therapeutic target for bladder cancer.
Keywords: bladder cancer, circular RNA, apoptosis, circ-Foxo3, miR-191