111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

金麦通通过抑制由链脲佐菌素诱导的糖尿病大鼠模型中的 TXNIP/NLRP3 炎性体激活,减轻了糖尿病周围神经病变
Authors Sun Q, Wang C, Yan B, Shi X, Shi Y, Qu L, Liang X
Received 19 July 2019
Accepted for publication 23 September 2019
Published 17 October 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 2145—2155
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S223842
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Juei-Tang Cheng
Background: Jinmaitong (JMT) has been used to prevent and treat diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) for decades. The present study aimed to elucidate the effects of JMT on thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) and Nod-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activation in the streptozotocin (STZ)-induced rat model.
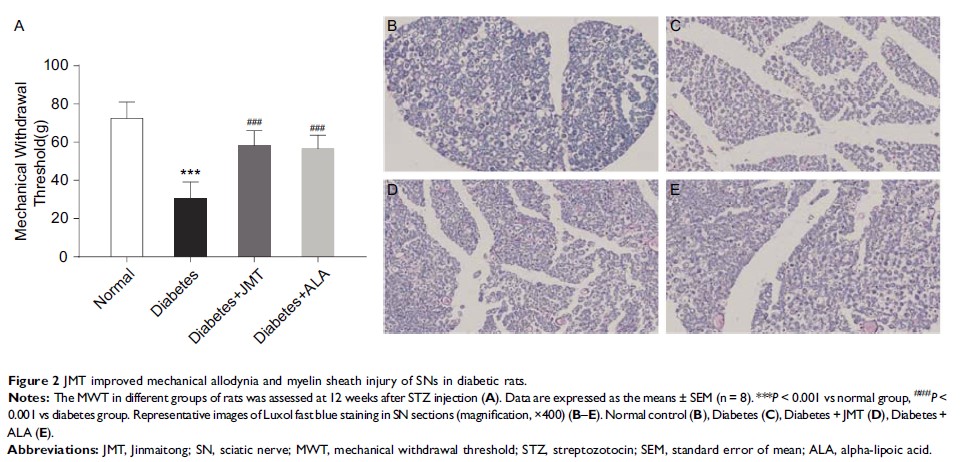
Methods: The diabetic rat model was induced by a single intraperitoneal injection of 55 mg/kg STZ. The rats were divided into 3 groups (n = 8–10 per group): diabetic control, JMT (0.876 g/kg/d), and alpha-lipoic acid (ALA; 100 mg/kg/d). Body weight and blood glucose levels were monitored every 4 weeks for 12 weeks. Mechanical allodynia and myelin sheath injury of sciatic nerves (SNs) were assessed using the mechanical withdrawal threshold (MWT) test and Luxol fast blue staining. Serum T-superoxide dismutase (T-SOD), malondialdehyde (MDA), and catalase (CAT) levels were measured using commercially available kits. TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome proteins, including TXNIP, NLRP3, pro-caspase-1, and cleaved -caspase-1, and the downstream protein interleukin (IL)-1β, were measured using immunohistochemistry and Western blot. Gasdermin D (GSDMDC1) protein expression was analyzed using Western blot, and serum IL-1β and IL-18 levels were detected using ELISA.
Results: JMT did not significantly affect body weight or level of fasting blood glucose but improved mechanical allodynia and myelin sheath injury of SNs at 12 weeks following treatment. Moreover, JMT increased serum levels of the anti-oxidative enzymes CAT and T-SOD, and decreased MDA levels. Both JMT and ALA decreased expression of TXNIP, NLRP3, and cleaved-caspase-1 protein. JMT and ALA also decreased IL-1β, IL-18, and GSDMDC1 protein expression.
Conclusion: The current study demonstrated that TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome activation is involved in the molecular mechanisms underlying JMT’s protective effects in the STZ-induced diabetic rat model, which provides novel evidence to support the future clinical use of JMT.
Keywords: Jinmaitong, diabetic peripheral neuropathy, TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome, diabetic rat model, alpha lipoic acid