111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

铂纳米颗粒作为葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的小鼠结肠炎的治疗剂
Authors Zhu S, Zeng M, Feng G, Wu H
Received 30 March 2019
Accepted for publication 28 September 2019
Published 18 October 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 8361—8378
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S210655
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate the anti-colitis potential of platinum nanoparticles (PtNPs).
Materials and methods: 5-, 30- and 70-nm PtNPs were administered to C57BL/6 mice once daily by intragastric gavage for 8 d during and after 5-d dextran sodium sulfate treatment.
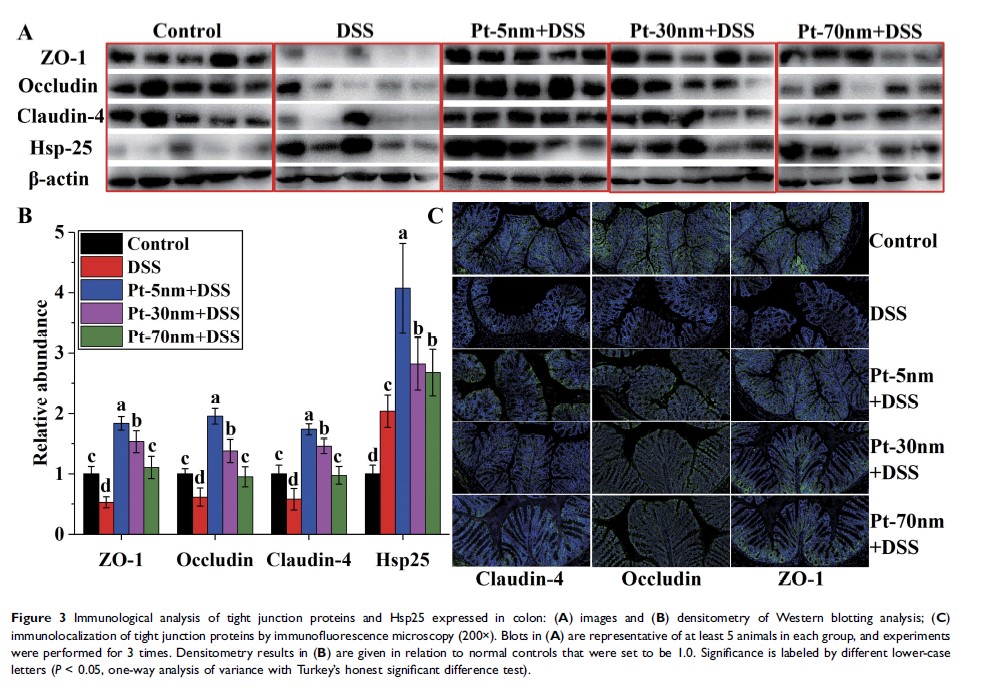
Results: According to body weight change, stool blood and consistency, and colon length and histopathology, PtNPs size-dependently alleviated DSS-induced murine colitis. PtNPs enhanced gut-barrier function by upregulating the colonic expressions of heat-shock protein 25 and tight junction proteins. Based on colonic myeloperoxidase activity, colonic and peripheral levels of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α, and peripheral counts of white blood cells, PtNPs attenuated colonic and systemic inflammation. By suppressing lipopolysaccharide-triggered production of proinflammatory mediators, including nitric oxide, tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-6, PtNPs exerted direct anti-inflammatory activities in RAW264.7 macrophages through a mechanism involving intracellular reactive oxygen species scavenging and Toll-like receptor 4/NF-κB signaling suppression. High-throughput 16S rRNA sequencing of fecal samples unveiled that PtNPs induced gut dysbiosis by unfavorably altering α-diversity, Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio, and richness of certain specific bacteria.
Conclusion: PtNPs are a promising anti-colitis agent, but may negatively impact gut-microbiota.
Keywords: platinum nanoparticles, ulcerative colitis, gut-microbiota, anti-inflammation, gut-barrier function