111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

豆甾醇通过减少氧化应激和使自噬失活来发挥抗缺血/再灌注损伤的神经保护作用
Authors Sun J, Li X, Liu J, Pan X, Zhao Q
Received 20 June 2019
Accepted for publication 9 September 2019
Published 18 October 2019 Volume 2019:15 Pages 2991—3001
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S220224
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Prof. Dr. Roumen Kirov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yu-Ping Ning
Purpose: Stroke remains the primary cause of pain, suffering, and death in patients. One of the major thrusts in stroke therapy is to find an effective prevention strategy. Objectives of this study are to testify the neuro-protection effect of stigmasterol in ischemic/reperfusion injury model.
Methods: The dosage-dependent effects (20, 40, and 80 mg/kg) of stigmasterol on physiological behaviors and oxidative stress biomarkers were investigated. Expression and phosphorylation of beclin1, microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 (LC3), adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK), mTOR, and N-terminal kinase (JNK) were detected.
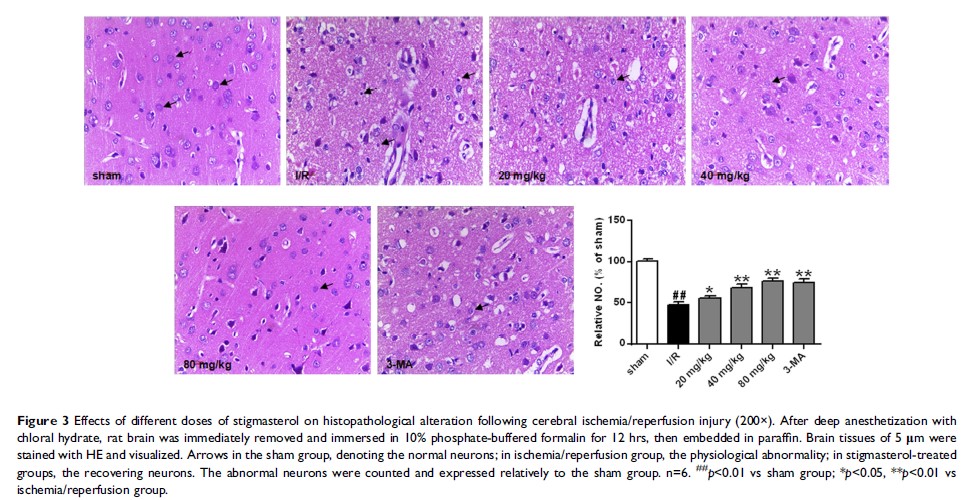
Results: The results showed that stigmasterol was able to effectively reduce neurological deficits and infarct damage induced by the ischemic/reperfusion injury, improve histopathology changes, and restore the levels of the endogenous antioxidant defense system in a dose–response mode. Stigmasterol effectively depressed the expression level of beclin1, and the conversion of LC3 I to LC3 II, while promoted the phosphorylation of mTOR, and remarkably inhibited the phosphorylation of AMPK and JNK, as well as the expression of JNK induced by 24 hrs of reperfusion.
Conclusion: These findings reveal that stigmasterol has neuro-protective effect against the ischemic/reperfusion injury, possibly associated with reduction of oxidative stress and inactivation of autophagy via AMPK/mTOR and JNK pathways.
Keywords: stigmasterol, ischemia/reperfusion injury, oxidative stress, autophagy, AMPK pathway, mTOR pathway, JNK pathway