111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

4-羟基-2-吡啶酮生物碱 Apiosporamide 可通过 PI3K/Akt 信号通路在骨肉瘤细胞中诱导凋亡
Authors Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Bao J, Huang J, Zhang H
Received 7 June 2019
Accepted for publication 20 September 2019
Published 21 October 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 8611—8620
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S218692
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Shreya Arora
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
Background: Osteosarcoma (OS) is a common primary malignant bone tumour in children and young adults. Apiosporamide, a 4-hydroxy-2-pyridone alkaloid from a deep-sea-derived fungus, Arthrinium sp. UJNMF0008, showed anti-proliferative effects toward a panel of human cancer cell lines, and the molecular mechanism in MG63 cells was then investigated in the current work.
Methods: Cell viability was determined with MTT method. Cell proliferation was detected using colony-formation assay. Screening electron microscope was used for morphology observation. Cell cycle and apoptosis was analysed via flow cytometry. Real-time PCR was conducted to evaluate the mRNA expression related with cell apoptosis. The expression levels of proteins related to capase-mediated apoptotic pathway and PI3K/Akt signalling pathway were detected by Western blotting.
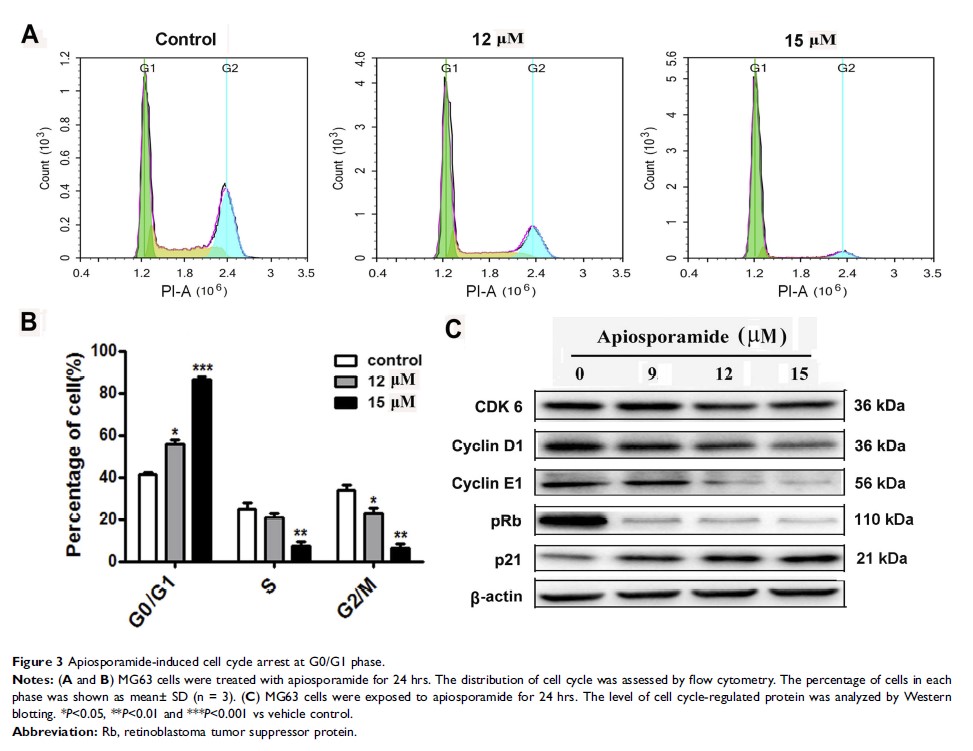
Results: Apiosporamide significantly decreased cell viability in cancer cells, and also exhibited excellent anti-proliferative effect. Apiosporamide caused cell cycle arrests at G0/G1 phase in MG63 cells. Moreover, apiosporamide induced apoptosis, activated caspase-3, caspase-8 and caspase-9, and regulated expression of Bax and Bcl-2 in MG63 cells. In addition, apiosporamide also attenuated PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.
Conclusion: Apiosporamide effectively suppressed MG63 cells proliferation by inducing apoptosis through PI3K/Akt and caspase-associated apoptotic pathway.
Keywords: apiosporamide, osteosarcoma, anti-proliferation, apoptosis, PI3K/Akt