111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

源自 G 蛋白偶联受体 124 的新型八肽通过促血管生成可改善慢性脑灌注不足引起的血管性痴呆大鼠模型的认知功能
Authors Xiao Y, Shen H, Li R, Zhou X, Xiao H, Yan J
Received 8 August 2019
Accepted for publication 2 October 2019
Published 23 October 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 3669—3682
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S226473
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Palas Chanda
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Manfred Ogris
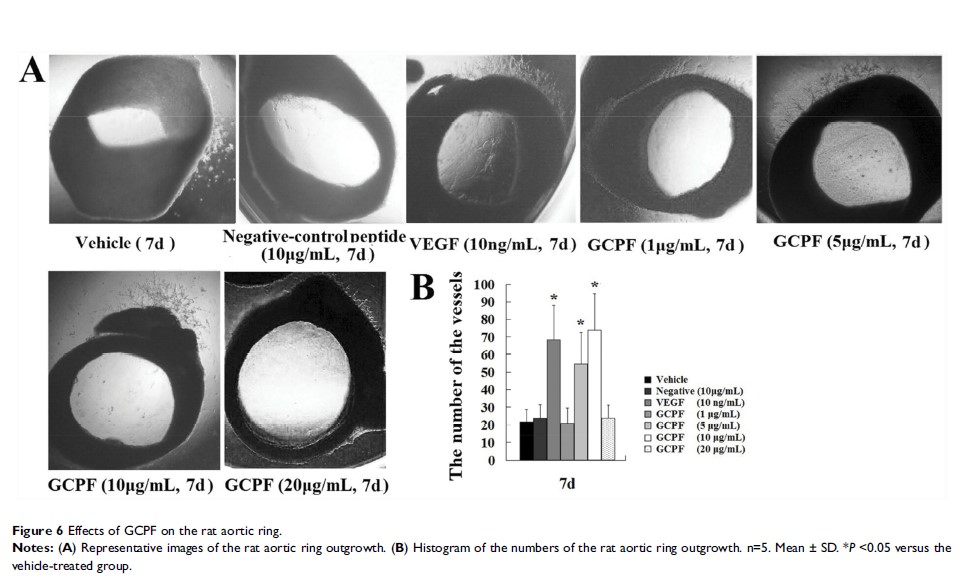
Purpose: The lack of effective therapies mandates the development of new treatment strategies for vascular dementia (VaD). G protein-coupled receptor 124 (GPR124) may be a therapeutic target for angiogenesis-related diseases of CNS, including VaD. The GCPF peptide is a truncated and screened fragment of the GPR124 extracellular domain. The potential use of GCPF for VaD treatment, angiogenesis and targeting of integrin αvβ3 are evaluated.
Methods and results: First, the in vivo results indicated that the GCPF peptide could decrease mean escape latency and increase platform crossing times in BCCAO rats. Second, the in vitro and ex vivo results indicated that the GCPF peptide was an active angiogenic peptide and could promote hCMEC/D3 cell migration and adhesion to ECM molecules. Third, in silico analyses predicted that GCPF could specifically interact with integrin αvβ3; the ∆G of GCPF binding to the binding pocket was −16.402 KJ/mol. The molecular characteristics indicated that highly hydrophilic GCPF with a pI of 11.70 had a short half-life in mammals (∼1 hr). Finally, the ELISA experiments indicated that low dissociation constant (Kd= 2.412±0.455 nM) corresponds to the high affinity of GCPF for integrin αvβ3.
Conclusion: The data indicate that adhesion of GCPF immobilized on ECM surface to endothelial cells via integrin αvβ3 modulates cellular functions to promote angiogenesis and improve cognitive function. This is the first report to prove that GCPF, a novel octapeptide, may be an effective strategy for VaD therapy.
Keywords: G-protein coupled receptor 124, vascular dementia, chronic cerebral hypoperfusion, angiogenesis, integrin, protein therapy