111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

SOX2 表达的增加预示着上尿路尿道上皮癌的不良预后并促进了恶性表型
Authors Bao Z, Zhan Y, He S, Li Y, Guan B, He Q, Yang X, Li X, Fang D, Zhou L
Received 15 June 2019
Accepted for publication 5 October 2019
Published 24 October 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 9095—9106
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S219568
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Teng
Background: The transcription factor SRY-related HMG-box 2 (SOX2) plays important regulatory roles in diverse biological processes (cell proliferation, migration, invasion and tumorigenicity). However, the relationship between SOX2 and upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC) have not been intensively investigated. This study aims to analyze the expression of SOX2 in UTUC as well as the predictive value for prognosis and the effect on tumor aggressiveness of SOX2.
Methods: Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded blocks containing samples from 341 patients with UTUC who underwent radical nephroureterectomy (RNU) at our institute were analyzed for SOX2 expression by immunohistochemistry (IHC). Associations between the SOX2 expression level and clinicopathological characteristics, disease-free survival (DFS) and cancer-specific survival (CSS) were analyzed. SOX2 expression in a normal urothelial cell line, urothelial carcinoma cell lines, 16 UTUC tissues and their pair-matched adjacent normal tissues was evaluated by RT-qPCR. Using RNA interference in vitro, the effects of SOX2 inhibition on cell proliferation, migration, invasion and tumorigenicity were determined.
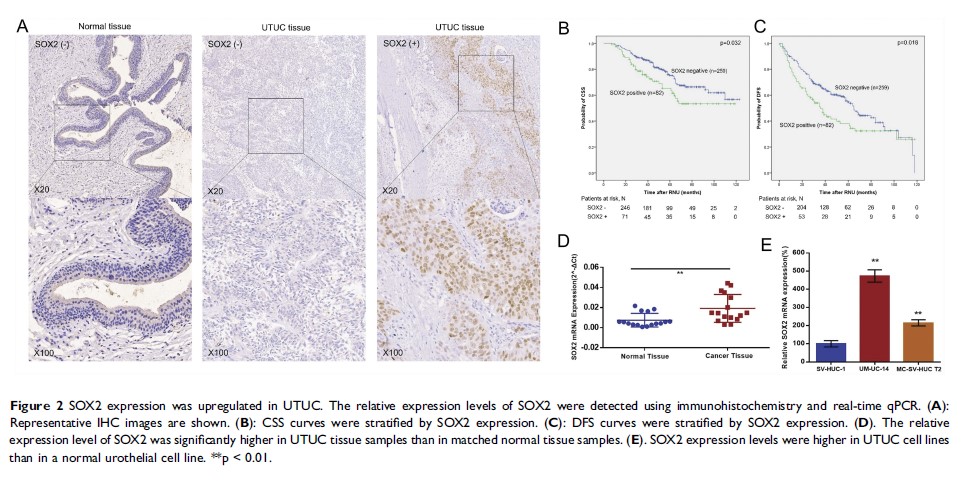
Results: SOX2 expression was significantly upregulated in UTUC tissue samples compared with paired-adjacent nontumorous tissue samples. SOX2 expression was correlated with important clinicopathological features, including tumor stage, tumor grade, tumor architecture and the presence of glandular or sarcoma differentiation, and was an independent predictor of poor DFS and CSS. Further experiments indicated that SOX2 expression was higher in UTUC cell lines than in a normal urothelial cell line. Knocking down SOX2 expression could inhibit malignant phenotypes (cell proliferation, stemness, migration, invasion and tumorigenicity) in UTUC cells.
Conclusion: SOX2 is an independent prognostic marker of poor DFS and CSS in UTUC patients who have undergone RNU. Moreover, these data suggest that SOX2 may be a promising therapeutic target in UTUC.
Keywords: SRY-related HMG-box 2, upper tract urothelial carcinoma, biomarker, prognosis, stemness