111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

曾接受异基因肝移植及免疫抑制治疗的患者的潘多拉孢子菌菌血症:一份病例报告
Authors Xiao X, Tian H, Cheng X, Li G, Zhou J, Peng Z, Li Y
Received 17 August 2019
Accepted for publication 12 October 2019
Published 25 October 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 3359—3364
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S227643
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Joachim Wink
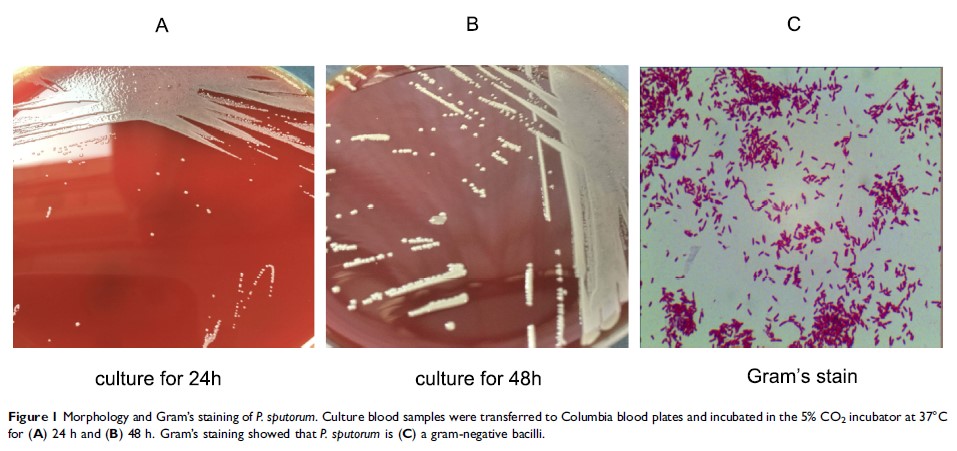
Abstract: Pandoraea sputorum (P. sputorum ), an emerging pathogen, is able to trigger a pronounced pro-inflammatory response that results in lung dysfunction in cystic fibrosis (CF) patients. All previous P. sputorum isolates have been obtained from the respiratory samples of CF patients, with no reported cases of P. sputorum bacteremia. For the first time, we report P. sputorum isolates recovered twice from the blood cultures of a patient with liver cancer who had undergone allogeneic liver transplantation. These isolates were successfully identified by combining mass spectrometry and molecular techniques based on 16S rRNA sequencing methods. At the onset of the P. sputorum bacteremia, the patient’s peripheral T, B and NK cell counts were 181.68/μL, 59.57/μL and 70.66/μL, respectively. The serum procalcitonin level, C-reactive protein level and peripheral neutrophil granulocyte percentage were 0.56 ng/mL, 61.00 mg/L and 96.8%, respectively. We found these isolates to be susceptible to ciprofloxacin and piperacillin/tazobactam and to be intermediate to amikacin. Previous studies have found P. sputorum isolates to be resistant. All of the data combined showed that compromised immune function from allogeneic liver transplantation plus immunosuppressive therapy contributes to the occurrence of P. sputorum bacteremia. Furthermore, the P. sputorum isolates demonstrated characteristic resistance profiles.
Keywords: Pandoraea sputorum , bacteremia, liver cancer, allogeneic liver transplantation