111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

色瑞替尼和艾乐替尼结合治疗与单独使用克唑替尼治疗间变性淋巴瘤激酶阳性的晚期非小细胞肺癌的成本-效果分析
Authors Liu M, Zhang L, Huang Q, Li N, Zheng B, Cai H
Received 16 July 2019
Accepted for publication 14 September 2019
Published 25 October 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 9195—9202
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S223441
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ahmet Emre Eskazan
Background: This study aimed to analyze the cost-effectiveness of crizotinib versus ceritinib or alectinib as first-line-targeted drug therapy for anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer in China.
Methods: The Markov model was used to simulate the medical cost and quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) of patients using crizotinib, ceritinib, or alectinib over a 10-year period by establishing three health states: progression-free, post-progression, and death. Randomized controlled clinical data were collected from the open-label, randomized phase 3 trials ALEX and ASCEND-4. Cost and utility values were derived from local charges and literature. Sensitivity analyses included one-way and probabilistic sensitivity analyses.
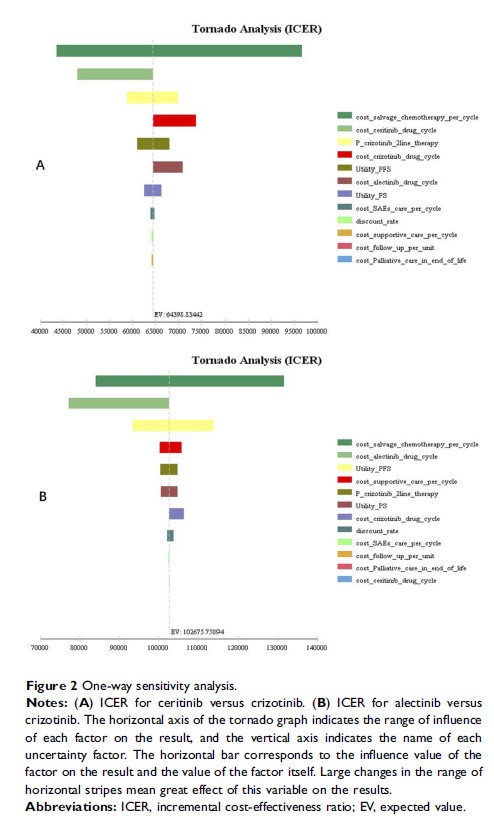
Results: Compared with patients who used crizotinib as first-line treatment, patients in the ceritinib and alectinib groups yielded an additional 1.32 and 3.30 QALYs with an incremental cost of $84,728.20 and $339,114.36, respectively. Thus, the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) was $64,398.83 and $102,675.74 per QALY in the ceritinib and alectinib groups, respectively. Alectinib was estimated to be more effective (4.68 QALY) and more costly ($432,063.06) with an ICER of $128,019.42 per QALY compared with ceritinib (2.69 QALY and $177,676.90). Results were robust to deterministic and probabilistic sensitivity analyses.
Conclusion: As a first-line treatment regimen, ceritinib and alectinib can extend the survival time of patients compared with crizotinib, but the medical cost also increases accordingly. According to the World Health Organization’s three-percent GDP measurement, first-line treatment with Crizotinib is the most cost-effective.
Keywords: crizotinib, ceritinib, alectinib, NSCLC, cost-effectiveness