111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

循环肿瘤细胞在肺癌中的预后价值:对 98 例中国患者的分析
Authors Tan MH, Zhong ZG, Chen PL, Zhou YX
Received 17 May 2019
Accepted for publication 30 August 2019
Published 25 October 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 8833—8840
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S216118
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Shreya Arora
Peer reviewer comments 6
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
Aim: To examine the prognostic values of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) in patients with advanced lung cancer.
Patients and methods: A total of 98 patients with their CTCs enumerated in 2017 was recruited. Data were retrieved from medical records for comparison. Patients’ overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) were studied using Kaplan-Meier curve with log rank test.
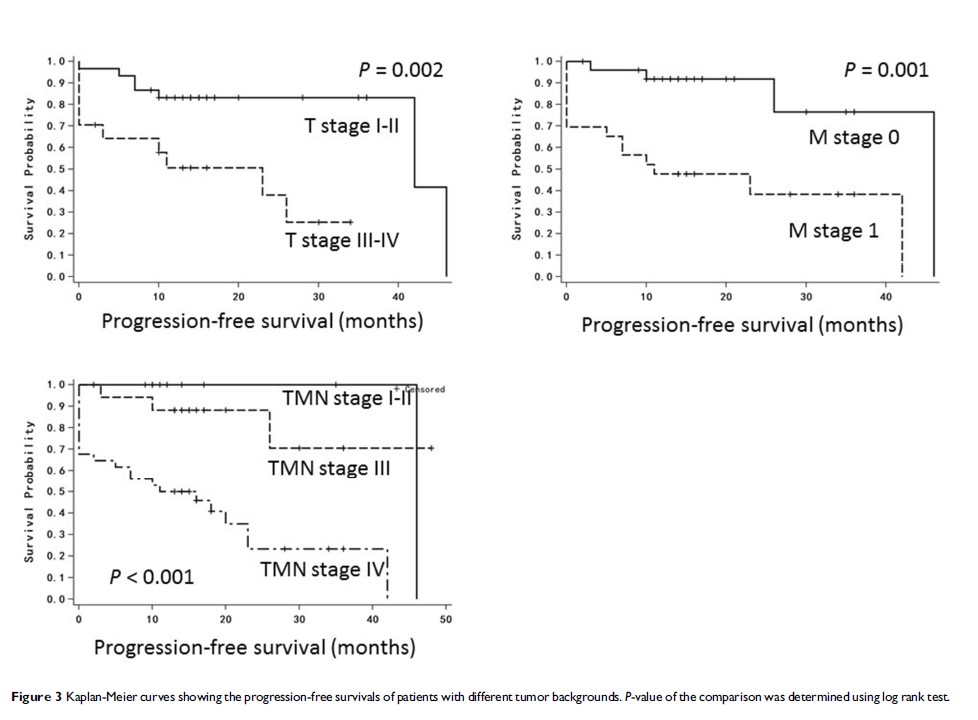
Results: Seventy-three percent of the patients were male, and nearly half of the patients (44.8%) were smokers. Most tumors were adenocarcinoma (73.4%), and about 60% of the cases were diagnosed at stage IV. Half of the patients showing less than nine CTCs. Patients’ OS were significantly associated with total CTC count (P =0.047), epithelial CTC count (P =0.027), mixed CTC count (P =0.004), and use of adjuvant chemotherapy (P =0.001). For PFS, it was strongly associated with tumor backgrounds (T stage, P =0.002; M stage, P =0.001; TMN stage, P <0.001), cancer biomarkers (CEA, P =0.004; CA125, P =0.004; CA153, P =0.045), and treatment strategy (surgical intervention, P =0.025; first-line chemotherapy, P <0.001).
Conclusion: The present study clearly indicated the significant associations between CTC and overall survival of patients with lung cancer.
Keywords: circulating tumor cells, survival, lung cancer, prognostic values