111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

circMMP9 的上调通过靶向 miR-1265/CHI3L1 轴促进骨肉瘤进展
Authors Pan G, Hu T, Chen X, Zhang C
Received 6 August 2019
Accepted for publication 5 October 2019
Published 29 October 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 9225—9231
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S226264
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Teng
Background: Osteosarcoma (OS) is a very aggressive cancer. Nevertheless, how circular RNA (circRNA) contributes to OS progression remains unclear. Here, we aimed to research the functions of circMMP9 in OS progression.
Methods: Gene expression was determined via qRT-PCR. siRNA was used to knock down circMMP9. Proliferation was analyzed using CCK8 and colony formation assays. Migration and invasion were measured using Transwell assay.
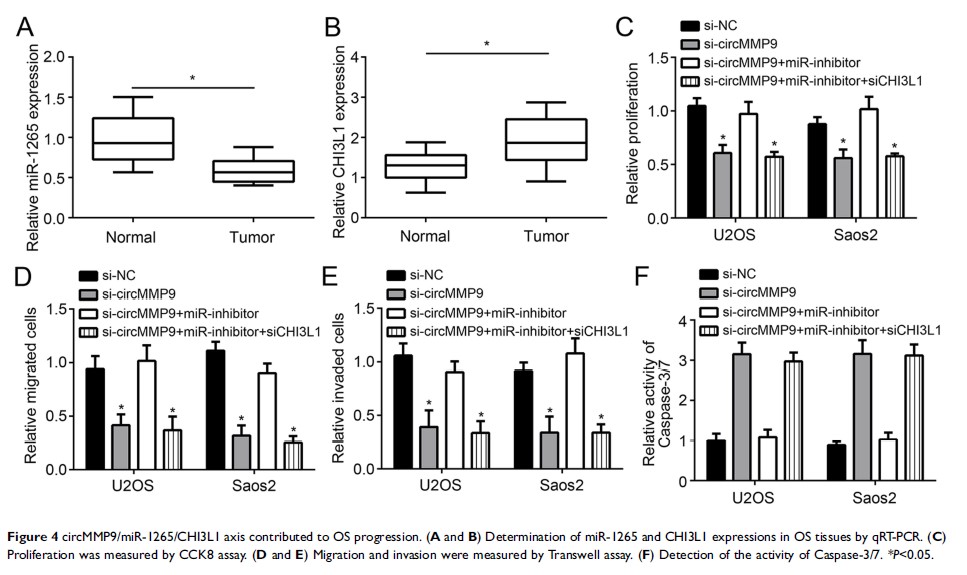
Results: circMMP9 was overexpressed in cancer tissues. Overexpressed circMMP9 was correlated with advanced tumor stage and predicted poor prognosis. circMMP9 knockdown exhibited a tumor-suppressive phenotype via suppressing proliferation, migration and invasion. Besides, decreased circMMP9 level promoted OS cellular apoptosis. Mechanistically, circMMP9 was shown to be located in the cytoplasm and sponge miR-1265. Furthermore, miR-1265 directly targeted CHI3L1. CHI3L1 levels were modulated by circMMP9/miR-1265 axis. Rescue experiments indicated that circMMP9 contributes to OS development through the miR-1265/CHI3L1 pathway.
Conclusion: Our findings provide a novel insight about how circRNA regulates OS progression.
Keywords: circMMP9, miR-1265, CHI3L1, osteosarcoma, progression