111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

胰腺导管腺癌:基于机器学习的定量计算机断层扫描纹理分析,用于组织病理学等级的预测
Authors Qiu W, Duan N, Chen X, Ren S, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Chen R
Received 7 June 2019
Accepted for publication 15 October 2019
Published 30 October 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 9253—9264
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S218414
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Nakshatri
Purpose: To assess the performance of combining computed tomography (CT) texture analysis with machine learning for discriminating different histopathological grades of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC).
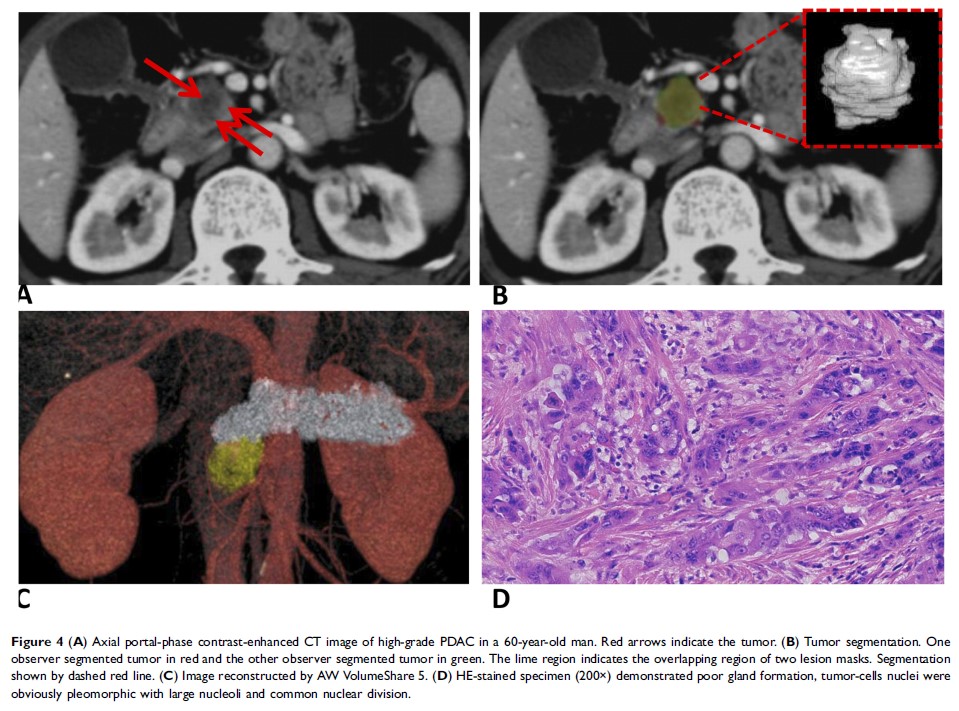
Methods: From July 2012 to August 2017, this retrospective study comprised 56 patients with confirmed histopathological PDAC (32 men, 24 women, mean age 64.04±7.82 years) who had undergone preoperative contrast-enhanced CT imaging within 1 month before surgery. Two radiologists blinded to the histopathological outcome independently segmented lesions for quantitative texture analysis. Histogram features, co-occurrence, and run-length texture were calculated. A support-vector machine was constructed to predict the pathological grade of PDAC based on preoperative texture features.
Results: Pathological analysis confirmed 37 low-grade PDAC (five well-differentiated/grade I and 32 moderately differentiated/grade II) and 19 high-grade PDAC (19 poorly differentiated/grade III) tumors. There were no significant differences in clinical or biological characteristics between patients with high-grade and low-grade tumors (P >0.05). There were significant differences between low-grade PDAC and high-grade PDAC on nine histogram features, seven run-length features, and two co-occurrence features. Cluster shade was the most important predictor (sensitivity 0.315). Using these texture features, the support-vector machine achieved 86% accuracy, 78% sensitivity, 95% and specificity.
Conclusion: Machine learning–based CT texture analysis accurately predicted histopathological differentiation grade of PDAC based on preoperative texture features, leading to maximization patient survival and achievement of personalized precision treatment.
Keywords: computed tomography, texture analysis, machine learning, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, histopathological grade