111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

羧甲基壳聚糖修饰的光响应性山茶皂角苷配基衍生物阳离子脂质体的制备及抑菌作用
Authors Zhang J, Ye CZ, Liu ZY, Yang Q, Ye Y
Received 2 June 2019
Accepted for publication 4 October 2019
Published 1 November 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 8611—8626
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S218101
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Background: Bacterial resistance to antibiotics is a persistent and intractable problem. The sapogenin isolated from the seeds of Camellia oleifera can inhibit antibiotic-resistant bacteria after structural modification.
Purpose: This study aims to improve sapogenin’s antibacterial activity and avoid bacterial resistance based on nano-preparation with photo responsiveness.
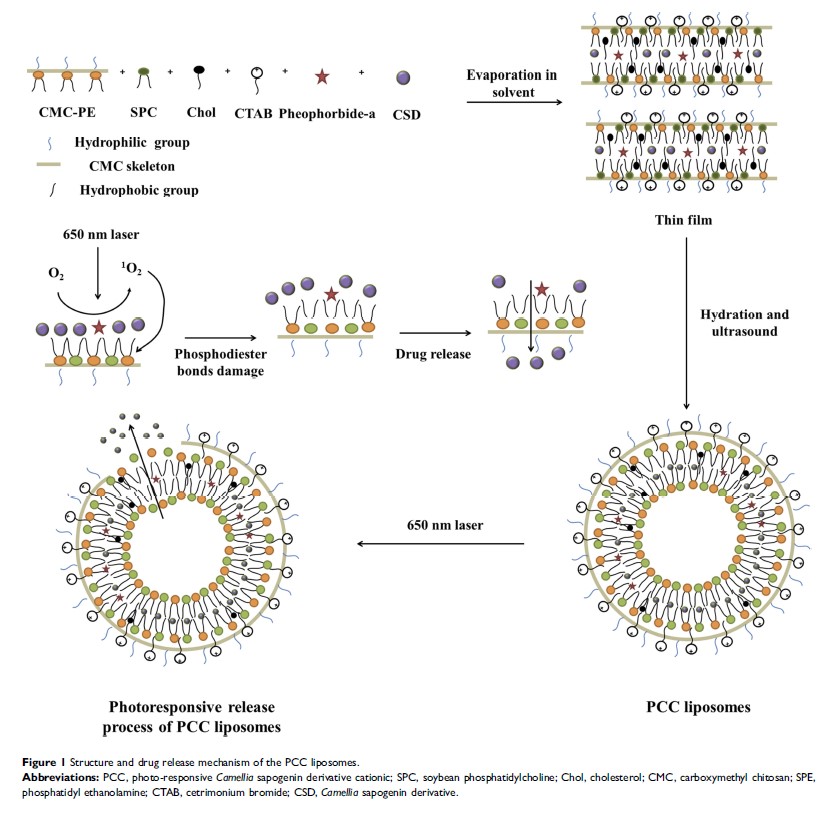
Methods: The liposome shell material of carboxymethyl chitosan-phosphatidyl ethanolamine (CMC-PE) was prepared using amidation reaction, and photo-responsive cationic (PCC) liposomes containing Camellia sapogenin derivative (CSD) and photosensitizer pheophorbide-a were prepared by film dispersion method. Encapsulation efficiency, drug loading, zeta potential, particle size distribution, morphology and stability of the PCC liposomes were determined by HPLC, particle size analyzer, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and fluorescence microscopy. Photo-responsive release of CSD in the PCC liposomes was determined by laser (0.5 mW/cm2) at 665 nm. Antibacterial activity of the PCC liposomes with or without irradiation was analyzed by MIC50, MBC, MBIC50, and bacterial morphology to evaluate the antibacterial effects on amoxicillin resistant Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus .
Results: Size distribution, zeta potential, encapsulation efficiency and drug loading of the PCC liposomes were 189.23 ± 2.12 nm, 18.80 ± 1.57 mV, 83.52 ± 1.53% and 2.83 ± 0.05%, respectively. The PCC liposomes had higher storage stability and gastrointestinal stability, and no obvious hemolytic toxicity to rabbit red blood cells and no cytotoxicity after incubation with Hela cells. The photosensitizer pheophorbide-a was uniformly dispersed in the phospholipid layer of the PCC liposomes and increased the CSD release after irradiation. The PCC liposomes could bind to bacteria and impaired their morphology and structure, and had significant bactericidal effect on amoxicillin resistant E. coli and S. aureus .
Conclusion: The photo-responsive PCC liposomes are efficient antibacterial agents for avoidance of bacterial resistance against antibiotics.
Keywords: Camellia sapogenin derivative, photo-responsive cationic liposomes, carboxymethyl chitosan, antibacterial effects, antibiotic substitutes