111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

用微小 RNA-129 靶向非小细胞肺癌中的 ZEB2,可通过调节 Wnt/β-Catenin 信号通路和上皮-间质转化抑制细胞增殖、侵袭和迁移
Authors Li X, Li C, Bi H, Bai S, Zhao L, Zhang J, Qi C
Received 29 May 2019
Accepted for publication 2 October 2019
Published 5 November 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 9165—9175
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S217536
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Rachel Predeepa
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
Introduction: Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a common cause of deaths all over the world. Emerging evidence has indicated that microRNA (miR) play key roles in NSCLC progression. We aimed to determine the functions of miR-129 in NSCLC. miR-129 was dramatically downregulated in NSCLC tissue samples and cells. The decreased miR-129 was found to be associated with poorer prognosis and malefic phenotype of NSCLC patients. We demonstrated that miR-129 upregulation could inhibit NSCLC cell growth. Furthermore, we also sought the molecular mechanism by which miR-129 repressed NSCLC development.
Methods: QRT-PCR was applied to detect the expressions of miR-129 in 51 pairs of NSCLC tissue samples. We further performed the Kaplan–Meier analysis to determine the association between miR-129 expressions and the survival rate of NSCLC patients. We then measured the expression levels of miR-129 in NSCLC cell lines. After that, MTT assays were performed to determine the influence of miR-129 on A549 cell proliferation. Transwell assay was then conducted to explore the biological functions of miR-129 in invasion and migration of NSCLC cells.
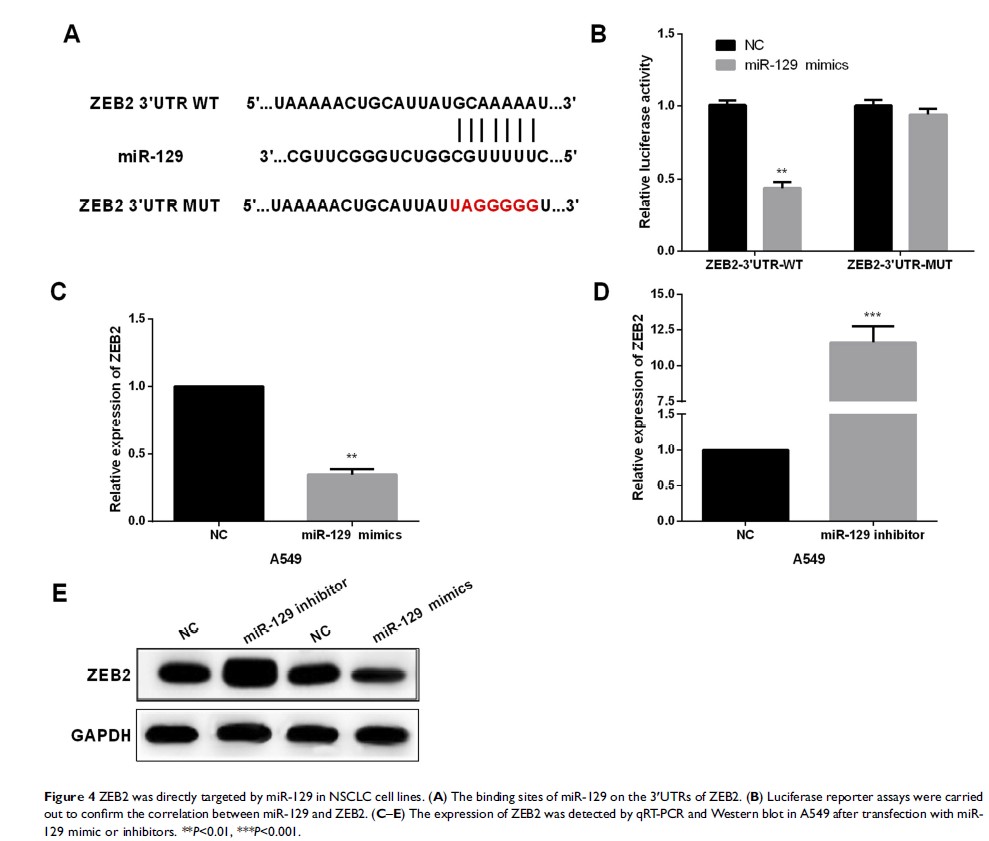
Results: Results showed that ZEB2 was directly targeted by miR-129 in NSCLC cell lines. Moreover, miR-129 restoration could inhibit EMT and Wnt/β-catenin in NSCLC cell lines.
Conclusion: In short, all these results indicated that miR-129/ZEB2 axis maybe a useful diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for NSCLC treatment.
Keywords: miR-129, ZEB2, NSCLC, Wnt/β-catenin, EMT