111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

LncRNA CCAT1 通过 miR-181b-5p/TUSC3 轴促进大肠癌的肿瘤发生
Authors Chen S, Liu Y, Wang Y, Xue Z
Received 22 May 2019
Accepted for publication 12 September 2019
Published 5 November 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 9215—9225
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S216718
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Shashank Kaushik (PT)
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
Aim: The aim was to determine the function and molecular mechanism of long non-coding RNA colon cancer associated transcript-1(lncRNA CCAT1) in the development of colorectal cancer (CRC).
Methods: CCAT1 mRNA expression levels were determined in CRC tissues and cells using reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Cell Counting Kit-8 and colony formation assays were used to examine the effects of CCAT1 on the proliferation of CRC cells. Luciferase reporter gene analysis was used to confirm the target gene of microRNA-181b-5p (miR-181b-5p) in CRC cells. Tumor xenografts were subsequently used to investigate the role of CCAT1 in CRC growth in vivo.
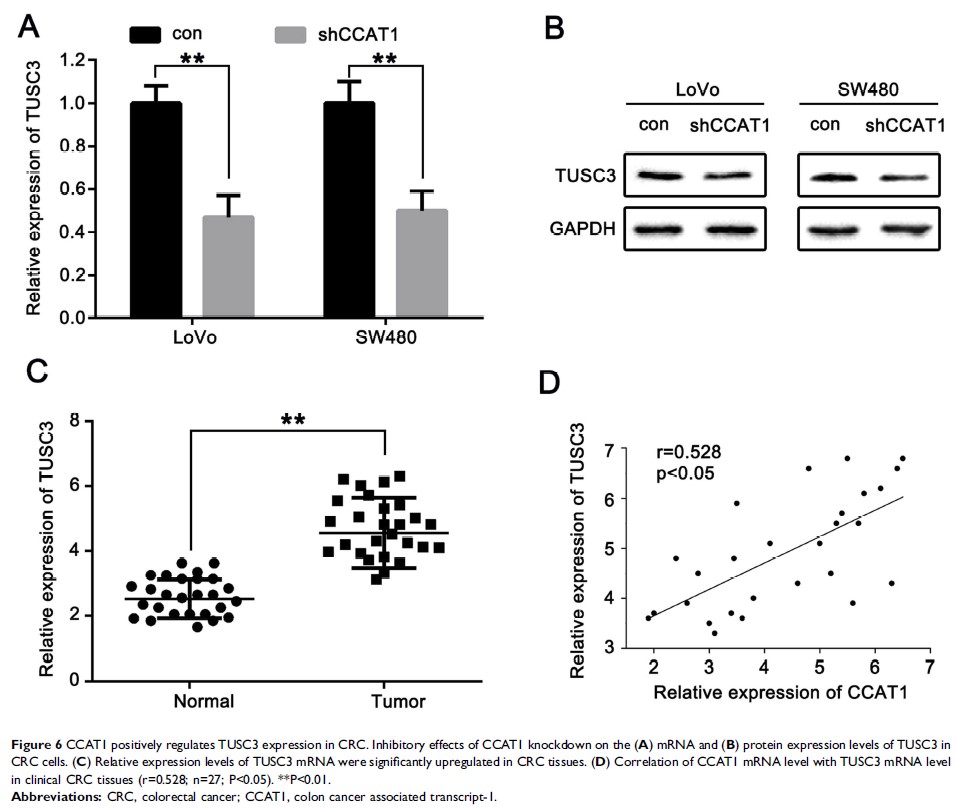
Results: The relative mRNA expression levels of CCAT1 were significantly higher in CRC tissues and cell lines compared with the normal tissues or cells. CCAT1 knockdown significantly inhibited CRC cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Bioinformatics and luciferase reporter assays showed that miR-181b-5p was a direct target of CCAT1, and the expression of miR-181b-5p was negatively correlated with the expression of CCAT1 in CRC tissues. Furthermore, CCAT1 positively regulated the level of tumor suppressor candidate 3 (TUSC3) by competing with miR-181b-5p in CRC cells.
Conclusion: These data suggested that lncRNA CCAT1 promoted colorectal cancer tumorigenesis via a miR-181b-5p/TUSC3 axis.
Keywords: LncRNA, CCAT1, CRC, miR-181b-5p, TUSC3