111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

对大肠癌细胞中抑制 XLF 和克服化学耐药性的天然化合物衍生物的鉴别
Authors Liu Z, Yu M, Fei B, Sun J, Wang D
Received 16 May 2019
Accepted for publication 27 September 2019
Published 6 November 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 3823—3834
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S215967
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristian Vilos
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Cristiana Tanase
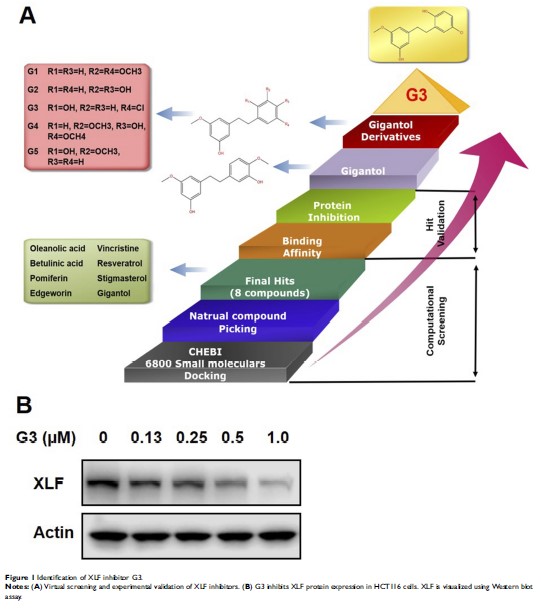
Purpose: A previous study has identified that XRCC4-like factor (XLF) is a potential target to overcome resistance to 5-fluorouracil (5-Fu) and oxaliplatin (OXA) in colorectal cancer (CRC). The purpose of this study is to develop potent XLF inhibitors to chemoresistance in CRC.
Methods: Virtual screening was adopted to identify novel XLF-binding compounds by initially testing 6800 molecules in Chemical Entities of Biological Interest library. Hit compounds were further validated by Western blot assay. Cell sensitivity to 5-Fu and OXA was measured using sulforhodamine B assay. The effect of XLF inhibitor on DNA repair efficiency was evaluated by comet assay, fluorescent-based nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) and homologous recombination (HR) reporter assays. DNA-binding activity of NHEJ key factors was examined by chromatin fractionation assay.
Results: We identified G3, a novel and potent XLF inhibitor (IC50 0.47±0.02 μM). G3 induced XLF protein degradation in CRC cells. Significantly, G3 improved cell sensitivity to 5-Fu and OXA in chemoresistant CRC cell lines. Mechanistically, G3 depleted XLF expression, severely compromised NHEJ efficiency by up to 65% and inhibited NHEJ key factor assembly on DNA. G3 also inhibited HR efficiency in a time-dependent manner.
Conclusion: These results suggest that G3 overcomes 5-Fu and OXA resistance in CRC cells by inhibiting XLF expression. Thus, XLF is a promising target and its inhibitor G3 is a potential candidate for treatment of chemoresistant CRC patients.
Keywords: virtual screening, XLF inhibitor, chemoresistance, colorectal cancer