111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

CD137 共同刺激可改善 LMP1 特异性嵌合抗原受体 T 细胞的体内和体外抗肿瘤作用
Authors Tang X, Tang Q, Mao Y, Huang X, Jia L, Zhu J, Feng Z
Received 27 June 2019
Accepted for publication 7 October 2019
Published 7 November 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 9341—9350
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S221040
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Rachel Predeepa
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leo Jen-Liang Su
Purpose: In previous research, we have found that LMP1-specific chimeric antigen (HELA/CAR) T cells can specifically recognize and kill LMP1-positive NPC cells. However, the tumor-inhibitory effectiveness of HELA/CART cells needs to be enhanced.
Methods: We created two CARs that contain the T cell receptor-ζ (TCR-ζ) signal transduction domain with the CD28 and CD137 (4-1BB) or CD134 (OX-40) intracellular domains in tandem (HELA/137CAR or HELA/134CAR). Then, the tumor-inhibitory functions of two new CAR-T cells were investigated, both in vitro and in vivo.
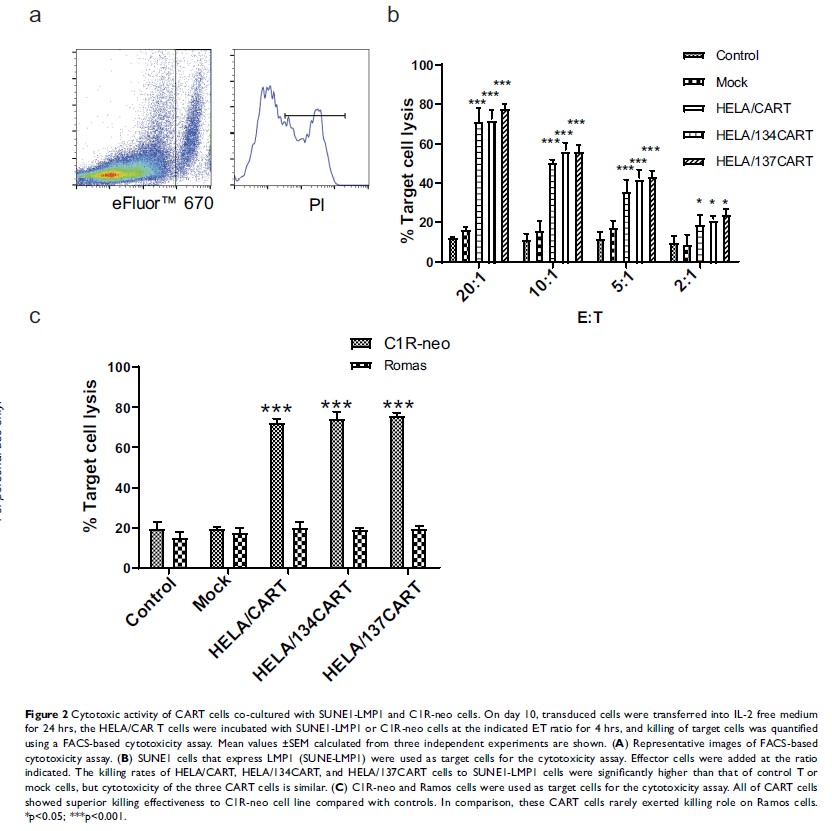
Results: The results showed that, after short-term expansion, primary human T cells were subjected to lentiviral gene transfer, resulting in large numbers of cells with >80% CAR expression. All CART cells were effective in killing SUNE1-LMP1 and C1R-neo cells, while HELA/137CART cells produced greater quantities of IFN-γ and IL-2 than HELA/CART cells. However, the level of IL-2 not INF-γ secreted by HELA/134CART cells was increased under the stimulation of LMP1 antigen. In an LMP1-positive NPC mouse xenograft model, HELA/137CART cells exhibited better antitumor activity and longer survival time in vivo compared with HELA/CAR T cells.
Conclusion: The findings suggest that CD137 and CD28 is a better costimulatory signaling domain than CD28 only for optimizing tumor-inhibitory roles.
Keywords: chimeric antigen receptors, LMP1, EBV, CD137