111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

急性缺血性中风患者的卒中相关性肺炎的个体化预测
Authors Huang GQ, Lin YT, Wu YM, Cheng QQ, Cheng HR, Wang Z
Received 28 July 2019
Accepted for publication 15 October 2019
Published 7 November 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 1951—1962
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S225039
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Zhi-Ying Wu
Background: Stroke-associated pneumonia (SAP) is a serious and common complication in stroke patients.
Purpose: We aimed to develop and validate an easy-to-use model for predicting the risk of SAP in acute ischemic stroke (AIS) patients.
Patients and methods: The nomogram was established by univariate and multivariate binary logistic analyses in a training cohort of 643 AIS patients. The prediction performance was determined based on the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) and calibration plots in a validation cohort (N=340). Individualized clinical decision-making was conducted by weighing the net benefit in each AIS patient by decision curve analysis (DCA).
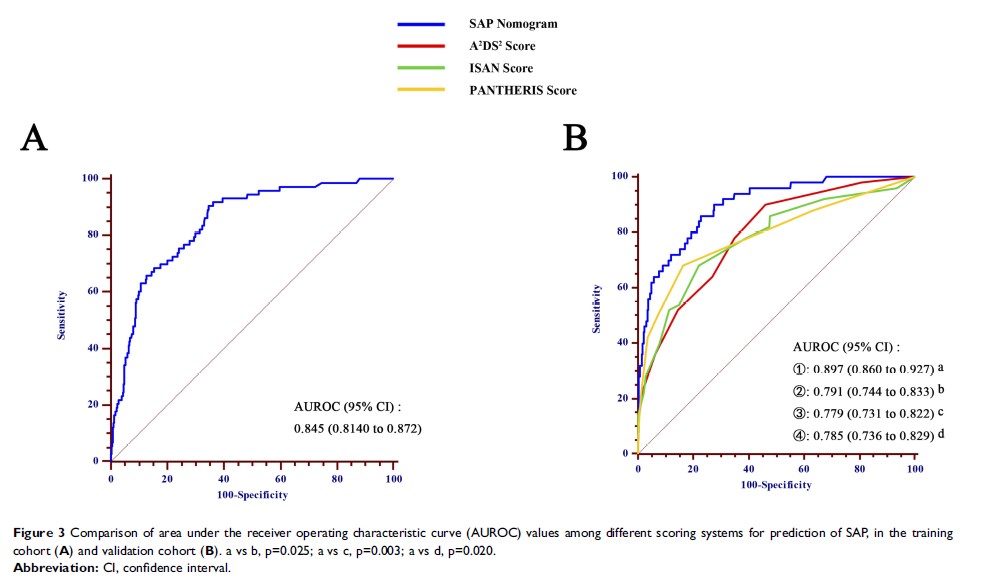
Results: Seven predictors, including age, NIHSS score on admission, atrial fibrillation, nasogastric tube intervention, mechanical ventilation, fibrinogen, and leukocyte count were incorporated to construct the nomogram model. The nomogram showed good predictive performance in ROC analysis [AUROC of 0.845 (95% CI: 0.814–0.872) in training cohort, and 0.897 (95% CI: 0.860–0.927) in validation cohort], and was superior to the A2DS2, ISAN, and PANTHERIS scores. Furthermore, the calibration plots showed good agreement between actual and nomogram-predicted SAP probabilities, in both training and validation cohorts. The DCA confirmed that the SAP nomogram was clinically useful.
Conclusion: Our nomogram may provide clinicians with a simple and reliable tool for predicting SAP based on routinely available data. It may also assist clinicians with respect to individualized treatment decision-making for patients differing in risk level.
Keywords: stroke-associated pneumonia, acute ischemic stroke, nomogram, prediction