111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

非小细胞肺癌患者对一线表皮生长因子受体酪氨酸激酶抑制剂耐药后,初始表皮生长因子受体酪氨酸激酶抑制剂治疗与 EGFR 外显子 19 缺失及 T790M 突变频率的相关性
Authors Gao W, He J, Jin SD, Xu J, Yu TF, Wang W, Zhu Q, Dai H, Wu H, Liu YQ, Shu YQ, Guo RH
Received 21 June 2019
Accepted for publication 25 October 2019
Published 8 November 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 9495—9504
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S220383
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Rachel Predeepa
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Nicola Silvestris
Background: The present study analyzed the relationship between clinical features and the T790M mutation in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients resistant to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) treatment.
Methods: NSCLC patients with resistance to first-generation EGFR-TKIs in which the disease control time was more than 6 months after initial TKI treatment were enrolled. T790M mutation analysis was performed using one of the following methods according to each manufacturer’s protocols: Cobas EGFR mutation test (41/105, 39.0%), digital PCR (42/105, 40.0%) or Scorpion amplification refractory mutation system (ARMS) (22/105, 21.0%). Sample type of T790M was from tissue only (53/105, 50.5%), plasma only (46/105, 43.8%), tissue and plasma (6/105, 5.7%).
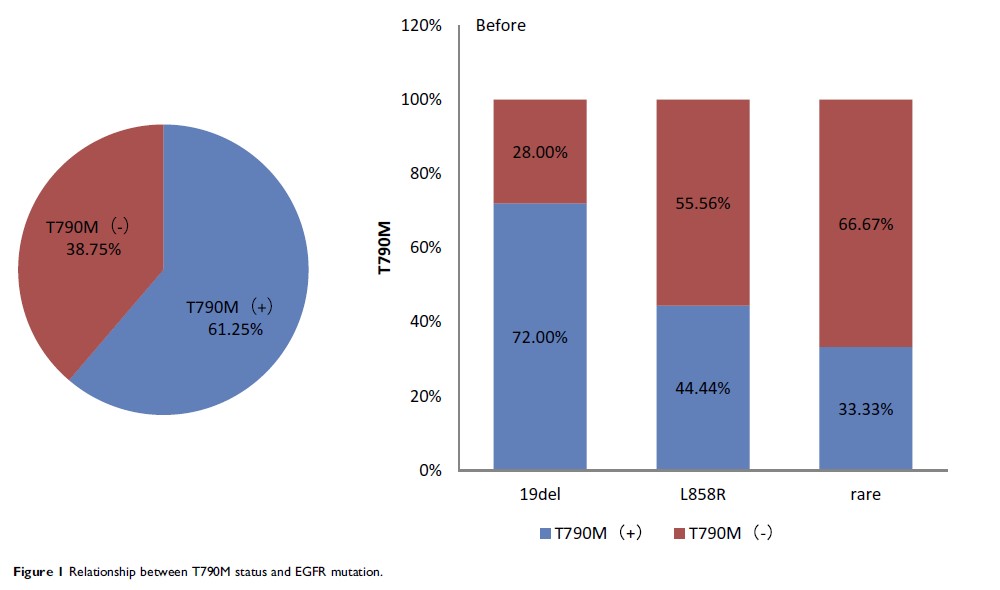
Results: Of 105 patients, 57 were T790M-positive and 48 were T790M-negative. T790M-positive patients had longer progression-free survival (PFS) after initial EGFR-TKI treatment (p = 0.019). T790M positivity was more frequent in patients treated with gefitinib than in those treated with icotinib (65% vs 40.54%, p = 0.018). The rate of T790M positivity was lower in patients with EGFR L858R (44.44%, 12/27) before TKI treatment than in those with EGFR 19del (72.0%, 36/50, p = 0.036). Patients who achieved PR after initial EGFR-TKI treatment had a higher rate of T790M positivity than those with SD (75.76% vs 50%, p = 0.023). There was no relationship between T790M status and age, gender, primary site, metastasis site, or treatment before TKI.
Conclusion: Progression-free survival (PFS), drug type, response to initial EGFR-TKI treatment, and EGFR status before initial EGFR treatment were associated with the frequency of T790M mutation.
Keywords: lung cancer, EGFR, T790M, gefitinib, icotinib