111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

在中国和美国使用派姆单抗治疗晚期复发性转移性头颈部鳞状细胞癌的成本效益分析
Authors Liu M, Han S, Zheng B, Cai H, Yang J, Zhuang Q, Li N
Received 6 August 2019
Accepted for publication 10 October 2019
Published 11 November 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 9483—9493
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S226243
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Chien-Feng Li
Background: Pembrolizumab, a programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) inhibitor, has recently gained prominence as a second-line treatment for recurrent and/or metastatic head and neck squamous cell cancer (R/M HNSCC). This study compares the acceptance and different influencing factors of pembrolizumab in the treatment of R/M HNSCC in developed (i.e., the United States) and developing (i.e., China) countries through cost-effectiveness analysis and provides valuable suggestions for clinical decision making.
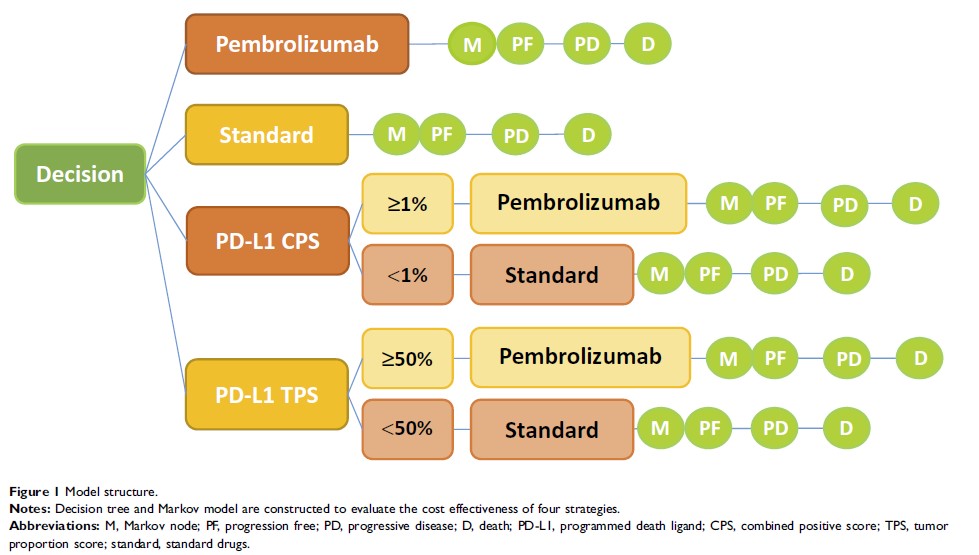
Methods: A Markov model was constructed using TreeAge Pro 2015 software to evaluate the economic value of four treatment strategies. Quality-adjusted life years (QALY) and incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) were used as economic indicators for incremental cost-effectiveness analysis. The stability of the model was evaluated by one-way sensitivity and probability sensitivity analyses.
Results: The ICERs for the pembrolizumab group versus PD-L1 CPS treatment in China and the US were $7892/QALY and $11,900/QALY, respectively. All ICERs were less than the threshold of $29,306 in China and $50,000 in the US; thus, pembrolizumab is cost effective. Sensitivity analysis confirmed a stable economic advantage in the single-drug regimen of pembrolizumab in China and the US.
Conclusion: Pembrolizumab monotherapy as a second-line treatment for R/M HNSCC presents more health benefits in comparison with the standard, PD-L1 TPS and PD-L1 CPS groups in China and the US.
Keywords: pembrolizumab, head and neck cancer, cost-effectiveness