111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

中国东南部人群非结核分枝杆菌肺部感染的流行病学:一项前瞻性监测研究
Authors Lin S, Wei S, Zhao Y, Lin J, Pang Y
Received 19 July 2019
Accepted for publication 30 October 2019
Published 12 November 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 3515—3521
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S223828
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Suresh Antony
Background: China is facing a great challenge of pulmonary nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) infections. This primary objective of this study was to assess the prevalence of NTM isolates among patients with presumptive TB in Fujian.
Methods: The mycobacterial isolates were collected from the tuberculosis survey from Fujian Province conducted between July 1, 2010 and June 30, 2011.
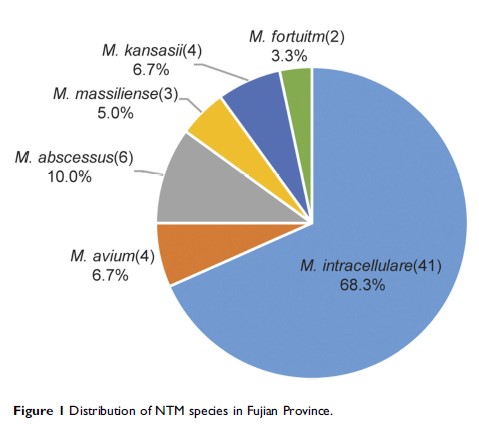
Results: From July 1, 2010 to June 30, 2011, 1425 isolates were included in the final analysis, of which 60 (4.2%) were identified as NTM species. M. intracellulare was the most frequently isolated NTM in Fujian, accounting for 68.3% of all NTM isolates. Compared with patients aged <45 years, patients aged 45–59 were more likely to have NTM infections. The education level of patients had an impact on the distribution of NTM infections. Illiterate patients had significantly higher odds of having NTM compared to literate patients. Patients with a previous TB episode had higher NTM risk as compared to those without previous TB episodes.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the predominant NTM is M. intracellulare among patients with presumptive TB in Fujian. In addition, elderly patients, those with a previous TB episode and illiterate patients have higher NTM risk.
Keywords: nontuberculous mycobacteria, prevalence, risk factor