111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

非小细胞肺癌中 EGFR T790M 突变与常见的 EGFR -激活突变并存的不良预后
Authors Gao X, Zhao Y, Bao Y, Yin W, Liu L, Liu R, Yu Z, Zhou X, Shuai J
Received 22 May 2019
Accepted for publication 9 October 2019
Published 13 November 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 9621—9630
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S216721
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Lu-Zhe Sun
Purpose: Previous studies have shown that the presence of EGFR T790M mutation may reduce the treatment efficacy of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in EGFR -mutant lung cancer. However, little is known about the clinical features and outcomes of EGFR T790M mutation in pretreated patients with NSCLC.
Patients and methods: The clinical features of EGFR -activating and T790M mutations were assessed in a large cohort of patients with EGFR-TKI-naïve NSCLC (all/EGFR mutations, n=16,347/7,687). The correlation between the pretreatment T790M mutation status and clinical outcomes was evaluated using univariate and multivariate analyses.
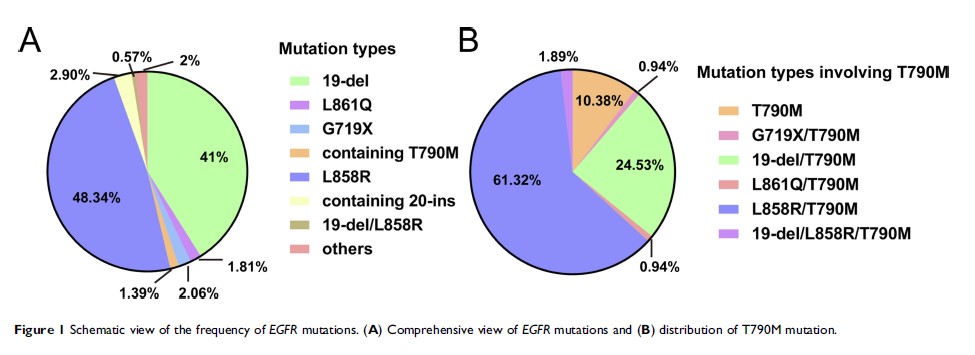
Results: Pretreatment T790M mutation was reported in 1.39% of the patients and coexisted with an EGFR -activating or uncommon mutation. The dual EGFR T790M and common EGFR -activating mutations were more likely to be detected in lung adenocarcinoma, whereas single T790M mutation was more prevalent in non-adenocarcinomas. The presence of de novo T790M mutation correlated with reduced recurrence-free survival (RFS) in patients with NSCLC (odds ratio [OR] 3.37, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.67–6.79, P = 0.001). After molecular stratification, T790M mutation was shown to exert adverse effects on the RFS of EGFR 19-del group (OR 2.89, 95% CI 1.10–7.91, P = 0.028) and EGFR L858R group (OR 3.43, 95% CI 1.33–8.88, P = 0.013). Furthermore, pretreatment T790M mutation promoted tumor metastasis to different sites.
Conclusion: T790M-positive tumors presented special clinical features, and the coexistence of T790M and common EGFR -activating mutations was associated with poor prognosis in patients with NSCLC.
Keywords: pretreatment T790M mutation, dual EGFR mutations, recurrence-free survival, non-small cell lung cancer