111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

沉默 MAGI1 可通过 Wnt/β-Catenin 和 PTEN/AKT 信号通路促进胶质瘤细胞的增殖并抑制其凋亡
Authors Lu Y, Sun W, Zhang L, Li J
Received 11 May 2019
Accepted for publication 15 October 2019
Published 13 November 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 9639—9650
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S215400
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Rachel Predeepa
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
Background: Membrane-associated guanylate kinase (MAGUK) with inverted orientation protein 1 (MAGI1) is a novel member of the MAGUK family with a vital role in tumor progression related to invasion and metastasis. However, the function of MAGI1 in glioma is currently unknown. We therefore analyzed the expression of MAGI1 protein in human glioma samples, glioma cell lines and glioma stem cells (GSCs), and explored its effects on glioma cell proliferation and apoptosis.
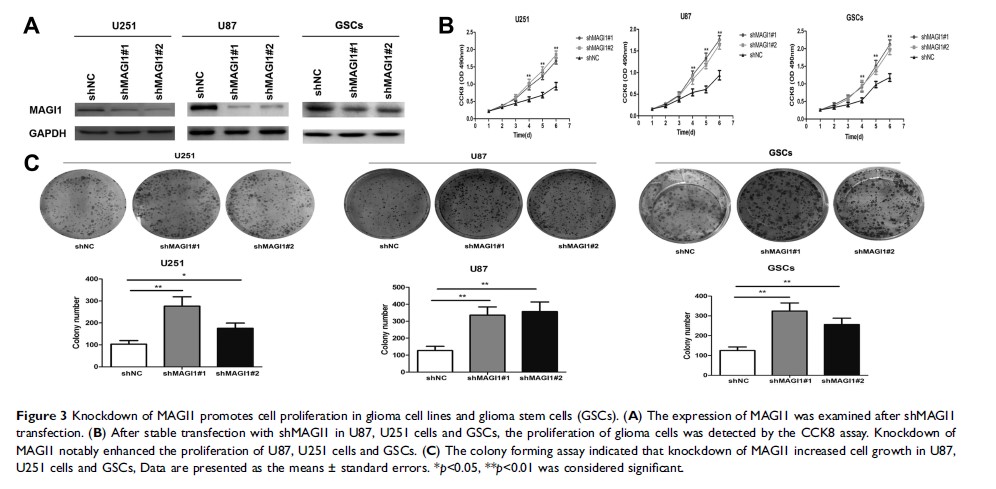
Methods: MAGI1 expression in glioma tissues was examined by Western blotting and real-time polymerase chain reaction and its relationships with clinical pathological features were analyzed. The effects of MAGI1 knockdown on the proliferation of glioma cell lines and GSCs were detected by CCK8 and colony-formation assays, and apoptosis was assessed by flow cytometry. We also investigated the effects of MAGI1 silencing on protein expression levels of epithelial-mesenchymal transition biomarkers, as well as β-catenin, cyclin D1, PTEN and phospho-Akt by Western blotting.
Results: MAGI1 was significantly downregulated in glioma tissues and its expression was related to cancer progression. Silencing of MAGI1 in both glioma cell lines and GSCs enhanced proliferation and inhibited apoptosis. MAGI1 knockdown also significantly increased the expression levels of N-cadherin, vimentin, β-catenin, cyclin D1 and phospho-Akt and reduced the expression of E-cadherin and PTEN.
Conclusions: Our results indicated that MAGI1 might play a vital role in glioma progression and may represent a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of glioma.
Keywords: glioma, MAGI1, β-catenin, EMT, proliferation, knockdown