111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

ESS,SACS,BQ 和 SBQ 对慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停的筛查价值
Authors Xiong M, Hu W, Dong M, Wang M, Chen J, Xiong H, Zhong M, Jiang Y, Liu D, Hu K
Received 18 July 2019
Accepted for publication 9 October 2019
Published 13 November 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 2497—2505
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S223354
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Chunxue Bai
Objective: To compare the performance of Epworth sleepiness scale (ESS), sleep apnea clinical score (SACS), Berlin questionnaire (BQ), and STOP-BANG questionnaire (SBQ) in screening for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Methods: A total of 431 patients were analyzed. All subjects completed lung function test, ESS, SACS, BQ, and SBQ survey and overnight polysomnography (PSG). According to lung function and PSG results, participants were divided into COPD with OSA group (OVS, AHI ≥5) and without OSA group (AHI <5). The value of ESS, SACS, BQ, and SBQ was compared in predicting OSA in patients with COPD by receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curve statistics.
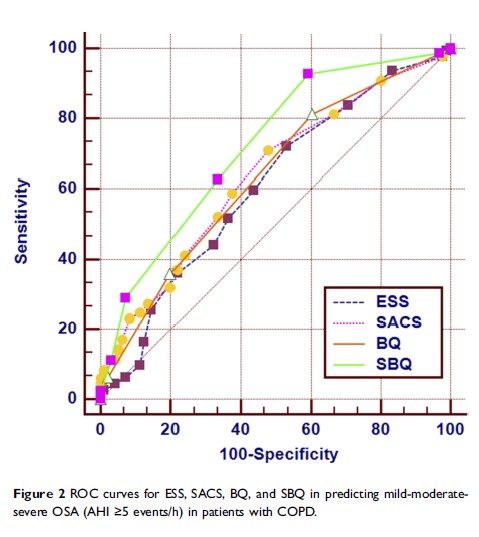
Results: Of the 431 subjects, there were 96 cases in COPD without OSA group, and 335 cases in OVS group including 183, 96, and 56 cases of COPD combined with mild, moderate or severe OSA. In predicting different degrees of severity of OSA in patients with COPD, the value of ESS was poor with all the values of area under the curve (AUC) < 0.7. SACS and BQ had moderate predictive value in screening for severe OSA with the value of AUC of 0.750, 0.735 respectively. However, the SBQ performed best in predicting various degrees of OSA. For screening mild OSA (AHI ≥5), the ROC statistics recommended the cut-off score of SBQ >2 was considered high risk of OSA; the sensitivity, specificity, and AUC were 92.8%, 40.6%, and 0.723 respectively, the odds ratio (OR) was 2.161. When AHI ≥15, AUC for SBQ was 0.737. In predicting severe OSA (AHI ≥30), the ROC curve showed cut-off point, sensitivity, specificity, and AUC for SBQ was >4, 66.1%, 82.1%, and 0.824 respectively; the positive and negative likelihood ratio was 3.70, 0.41 separately, the OR was 2.977.
Conclusion: SBQ performed better than ESS, SACS, and BQ in predicting OSA in patients with COPD.
Keywords: Berlin questionnaire, STOP-BANG questionnaire