111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

ATHENA: A Phase 3, Open-Label Study Of The Safety And Effectiveness Of Oliceridine (TRV130), A G-Protein Selective Agonist At The μ-Opioid Receptor, In Patients With Moderate To Severe Acute Pain Requiring Parenteral Opioid Therapy
Authors Bergese SD, Brzezinski M, Hammer GB, Beard TL, Pan PH, Mace SE, Berkowitz RD, Cochrane K, Wase L, Minkowitz HS, Habib AS
Received 30 May 2019
Accepted for publication 19 October 2019
Published 14 November 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 3113—3126
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S217563
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Nicola Ludin
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Katherine Hanlon
Background: Pain management with conventional opioids can be challenging due to dose-limiting adverse events (AEs), some of which may be related to the simultaneous activation of β-arrestin (a signaling pathway associated with opioid-related AEs) and G-protein pathways. The investigational analgesic oliceridine is a G-protein-selective agonist at the μ-opioid receptor with less recruitment of β-arrestin. The objective of this phase 3, open-label, multi-center study was to evaluate the safety and tolerability, of IV oliceridine for moderate to severe acute pain in a broad, real-world patient population, including postoperative surgical patients and non-surgical patients with painful medical conditions.
Methods: Adult patients with a score ≥4 on 11-point NRS for pain intensity received IV oliceridine either by bolus or PCA; multimodal analgesia was permitted. Safety was assessed using AE reports, study discontinuations, clinical laboratory and vital sign measures.
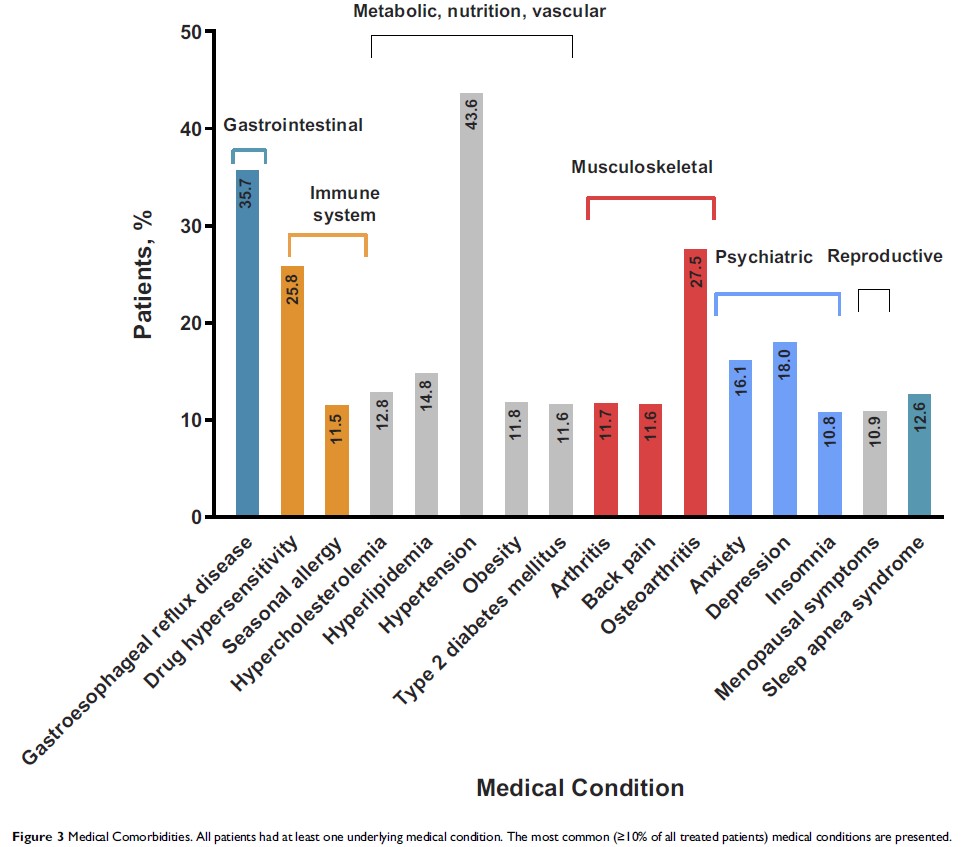
Results: A total of 768 patients received oliceridine. The mean age (SD) was 54.1 (16.1) years, with 32% ≥65 years of age. Most patients were female (65%) and Caucasian (78%). Surgical patients comprised the majority of the study population (94%), most common being orthopedic (30%), colorectal (15%) or gynecologic (15%) procedures. Multimodal analgesia was administered to 84% of patients. Oliceridine provided a rapid reduction in NRS pain score by 2.2 ± 2.3 at 30 mins from a score of 6.3 ± 2.1 (at baseline) which was maintained to the end of treatment. No deaths or significant cardiorespiratory events were reported. The incidence of AEs leading to early discontinuation and serious AEs were 2% and 3%, respectively. Nausea (31%), constipation (11%), and vomiting (10%) were the most common AEs. AEs were mostly of mild (37%) or moderate (25%) severity and considered possibly or probably related to oliceridine in 33% of patients.
Conclusion: Oliceridine IV for the management of moderate to severe acute pain was generally safe and well tolerated in the patients studied.
ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT02656875.
Keywords: acute pain, analgesia, patient-controlled, clinical trial