111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

鼻窦鳞状细胞癌患者术前中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞比率的预后价值
Authors Zhong B, Deng D, Du JT, Chen F, Liu YF, Liu SX
Received 15 September 2019
Accepted for publication 10 November 2019
Published 15 November 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 9733—9741
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S231085
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Sandhya Gopi
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
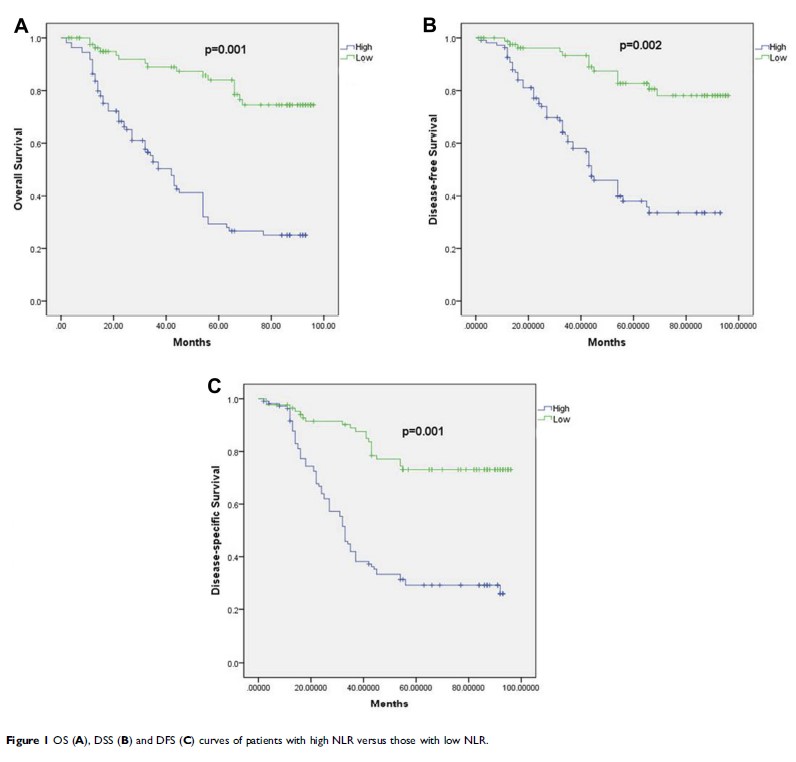
Objective: This study explored the effectiveness of a new inflammatory prognostic system, using preoperative neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) to predict the postoperative survival rate of patients with sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma (SSCC).
Methods: Patients diagnosed with SSCC who undergone surgically treated without neoadjuvant therapy were included in the study between May 2008 and October 2017. Preoperative NLR is defined as: preoperative neutrophil/postoperative lymphocyte ratio. The prognostic value was uncovered by univariate and multivariate Cox hazards analysis.
Results: A total of 147 patients were included in this study. Through the multivariate analysis, pathological T stage (hazard ratio [HR] 1.719, confidence interval [CI] 1.277–3.642, p<0.001), pathological N stage (HR 1.344, 95% CI 1.015–2.776, p<0.001), and preoperative NLR (HR 1.579, 95% CI 1.217–3.092, p=0.002) were independent risk factor for overall survival (OS). Pathological T stage (HR 1.835, 95% CI 1.141–3.132, <0.001), pathological N stage (HR 1.281, 95% CI 1.169–2.476, p<0.001), and preoperative NLR (HR 1.688, 95% CI 1.162–3.363, p p<0.001) were also independently associated with disease-free survival (DFS). Pathological T stage (HR p<0.001, 95% CI 1.537–3.021, p<0.001), pathological N stage (HR1.571, 95% CI 1.157–2.258, p<0.001), and preoperative NLR (HR 1.509, 95% CI 1.153–3.104, p=0.001) were independent risk factors for disease-specific survival (DSS).
Conclusion: The preoperative NLR is considered to be a useful predictor of postoperative survival in SSCC patients.
Keywords: sinonasal carcinoma, albumin-to-globulin ratio, patients, risk factor, survival